An Essential Guide to Cloud Migration Phases

Why Understanding Cloud Migration Phases Matters for Your Business
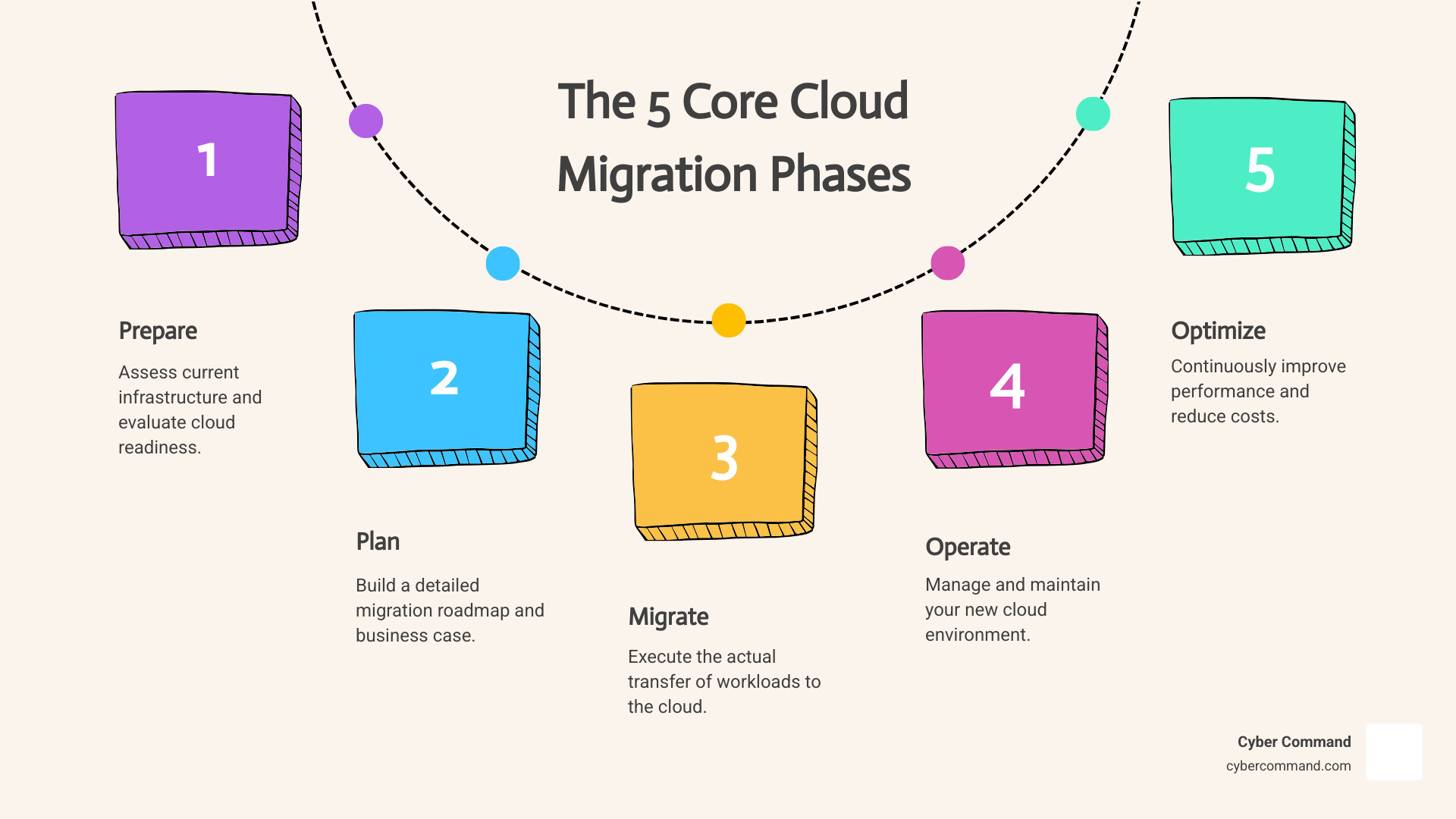
Cloud migration phases are the structured stages organizations follow to move their IT infrastructure, applications, and data from on-premises systems to the cloud. Most successful migrations follow five core phases:
- Prepare – Assess your current infrastructure and evaluate cloud readiness
- Plan – Build a detailed migration roadmap and business case
- Migrate – Execute the actual transfer of workloads to the cloud
- Operate – Manage and maintain your new cloud environment
- Optimize – Continuously improve performance and reduce costs
These phases aren’t just a checklist—they’re a proven framework that minimizes risk and maximizes the business value of your cloud investment.
The stakes are high. Without a structured approach, businesses face spiraling costs, security vulnerabilities, and operational disruptions. Research shows that companies migrating to the cloud see an average of 20% cost reduction and 43% faster time to market—but only when they follow a disciplined, phased methodology.
The data tells a compelling story. Gartner forecasts that spending on public cloud services will reach $679 billion in 2024, a 20.4% increase from the previous year. More than 50% of enterprise workloads now run in the public cloud, according to Flexera’s 2024 State of the Cloud Report. Yet many businesses struggle with the transition because they lack a clear roadmap.
Cloud migration isn’t a one-time project—it’s a change journey. The phased approach helps you build team confidence, prove value with early wins, and avoid the common pitfalls that derail migrations: unexpected costs, extended downtime, and security gaps.
The good news? You don’t have to steer this alone. Understanding the Benefits of Moving to the Cloud is just the first step. A structured migration strategy turns cloud computing from a source of stress into a competitive advantage.
I’m Reade Taylor, Founder and CEO of Cyber Command, and I’ve spent over two decades helping businesses steer complex technology changes, including guiding organizations through all cloud migration phases from initial assessment to post-migration optimization. My team and I have seen how a disciplined, phased approach transforms cloud migrations from risky ventures into strategic wins.
Why a Phased Approach to Cloud Migration is Crucial
Migrating to the cloud can feel like a monumental task, especially when dealing with complex IT environments. It’s a journey that can be intimidating due to the sheer volume of change management required. That’s why adopting a phased approach to cloud migration phases isn’t just a good idea—it’s crucial for success.
A phased approach offers several key advantages:
- Minimizing Risk: By breaking the migration into smaller, manageable chunks, we can identify and mitigate issues early, rather than facing a “big bang” failure. This iterative process allows us to learn and adapt.
- Reducing Downtime: A gradual transition means less disruption to your business operations. We can schedule migrations for non-critical periods or implement strategies for near-zero downtime, ensuring business continuity.
- Building Team Confidence: Starting with less complex applications allows our team to gain valuable experience and confidence. This builds foundational knowledge and helps us identify any skill or process gaps before tackling mission-critical systems.
- Ensuring Business Continuity: Phased migration allows us to maintain essential services throughout the transition, ensuring that your customers and employees continue to have access to the resources they need.
Without a well-defined plan and a phased approach, organizations often face significant challenges:
- Lack of Strategy: A clear cloud migration strategy is a well-defined plan that outlines the processes needed to move your data, applications, and infrastructure to a cloud-based environment. Without it, migration efforts can become chaotic and inefficient. Our research shows that a lack of strategy is a primary reason for cloud migration failures.
- Uncontrolled Costs: Unexpected expenses can quickly derail a migration project. A phased approach allows for better cost management, enabling us to set clear Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) and estimate future cloud costs more realistically.
- Security Vulnerabilities: Moving to the cloud introduces new security considerations. Without careful planning and a phased approach, security gaps can emerge, increasing the risk of data breaches and compliance issues. Identity, in particular, has become a critical third phase of security operations in the cloud era, demanding our attention.
- Vendor Lock-in: Without proper planning, organizations might inadvertently become too dependent on a single cloud provider, making future transitions difficult and costly.
These challenges highlight the importance of expert guidance. Our IT Project Management Services are designed to steer these complexities, ensuring a smooth and strategic transition for your business.
The 5 Essential Cloud Migration Phases Explained
The journey to the cloud is best understood as a series of deliberate steps, each building on the last. These five cloud migration phases—Prepare, Plan, Migrate, Operate, and Optimize—form a holistic framework for successful cloud change. This isn’t a linear race; it’s an iterative process where lessons learned in one phase inform and improve subsequent ones, much like the AWS Well-Architected Migration Lifecycle emphasizes.

Phase 1 & 2: Preparing and Planning Your Cloud Migration Phases
The initial stages of any successful cloud migration are all about thorough groundwork. We combine “Prepare” and “Plan” because they are deeply intertwined, laying the strategic and tactical foundations for everything that follows.
Preparation is about understanding where you are and where you want to go:
- Assessment of current infrastructure: We begin by evaluating your existing IT infrastructure. This involves collecting configurations, usage, and behavior data from your servers to understand your workloads inside out. This detailed view of your data center footprint is crucial for dependency mapping and migration wave planning.
- Readiness evaluation and skills gap analysis: We assess your team’s experience with cloud services, migration tools, and cutover processes. If there are knowledge gaps, we identify them and recommend targeted training. When needed, we can also bring in external expertise to validate your strategy and accelerate your progress.
- Defining business objectives and TCO analysis: Every migration should be driven by clear business goals, whether it’s cost savings, increased agility, or improved performance. We help you build a compelling business case for each workload, including a Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) analysis. For example, Google Cloud offers a free findy and assessment to help estimate potential migration costs and options, a practice we echo in our own services.
Planning translates your preparation into an actionable roadmap:
- Creating a detailed migration roadmap: This is where we define the specific order, timing, and approach for migrating workloads. It’s a process of translating high-level strategies into actionable deployment sequences.
- Dependency mapping: This is perhaps one of the most critical steps. We find and map all dependencies between your applications, databases, and other components. Grouping workloads by these relationships helps prevent service disruptions and ensures that all necessary components move together.
- Cloud Migration Checklist: A comprehensive checklist ensures no stone is left unturned. This includes systematically documenting dependency groups and validating their completeness.
- Choosing a data migration path: Data is the lifeblood of your business, so its migration needs careful consideration. We determine the best path based on network availability, data volumes, and sensitivity.
- Network Connections: For secure and fast transfers, especially for large volumes, dedicated connections like ExpressRoute (for Azure) or VPNs are often preferred. For smaller, less sensitive data, the public internet might suffice.
- Data Volumes: For massive datasets, offline options like Azure Data Box, which is a physical device shipped to your location, can be more efficient than online transfers.
- Defining a rollback plan: What happens if something goes wrong? A rollback plan is your safety net. We define what constitutes a failed deployment and create detailed, workload-specific instructions to revert to the previous stable state. Automating these steps in CI/CD pipelines and rigorously testing them is paramount.
- Stakeholder engagement and approval: A successful migration requires buy-in from all corners of your organization. We document the migration plan with clear business justifications, present tested rollback procedures, and validate schedules against business constraints. Securing formal approval and clear rollback authority from stakeholders is a non-negotiable step, as outlined in Microsoft’s Cloud Adoption Framework for planning.
Phase 3: The Migrate Phase
With meticulous preparation and planning complete, the “Migrate” phase is where the rubber meets the road. This is the actual execution of moving your IT assets to the cloud.
- Choosing a migration method: For each workload, we select the appropriate migration method.
- Downtime vs. Near-Zero Downtime: Non-critical workloads might tolerate planned outages (downtime migration), which is simpler. However, for critical, customer-facing applications, we implement near-zero downtime migration strategies, often involving continuous data replication to keep services operational throughout the transition.
- Data migration approach: This involves the actual transfer of your data. Depending on the path chosen in the planning phase, we use various tools and techniques to ensure data integrity and security. NetApp’s SnapMirror technology, for example, offers seamless data replication and continuous synchronization for ongoing migrations.
- Pilot migrations: We often start with pilot migrations—moving a small set of non-critical applications or non-production environments first. This allows us to test the full migration process, validate our assumptions, and refine our approach without impacting core business functions. Think of it as a dress rehearsal for the main event!
- Executing migration waves: Based on dependency mapping, we execute migration in waves, grouping related workloads together. We typically start with simpler, more predictable workloads, moving non-production environments before production, and scheduling critical systems after demonstrating initial success.
- Monitoring progress: Throughout the migration, continuous monitoring is essential. We track progress, ensure applications perform as expected in the new cloud environment, and quickly address any issues that arise.
For large-scale transfers, especially for businesses considering a full transition, our More info about Data Center Migration to Cloud services can provide comprehensive support and expertise.
Phase 4 & 5: Operating and Optimizing Post-Cloud Migration Phases
Once your workloads are successfully migrated, the journey doesn’t end. In fact, some of the most significant benefits of cloud computing are realized in the “Operate” and “Optimize” cloud migration phases.
Operating in the cloud involves managing your new environment effectively:
- Managing workloads in the cloud: This includes day-to-day administration, resource provisioning, and ensuring your applications run smoothly. Our managed IT services are designed to handle these complexities, allowing your internal teams to focus on strategic initiatives.
- Monitoring performance and availability: We continuously monitor your cloud environment to ensure applications meet performance benchmarks and remain highly available. This includes tracking resource utilization, identifying bottlenecks, and proactively addressing potential issues.
- Maintaining security and compliance: Cloud security is a shared responsibility. We ensure your cloud infrastructure adheres to industry best practices and regulatory requirements. This includes configuring access controls, implementing threat detection, and managing vulnerabilities. Identity has become a critical focal point in cloud security, often referred to as the “third phase of security operations,” requiring robust management and monitoring to prevent sophisticated cyber threats. For more insights on safeguarding your cloud environment, explore our More info about Cloud Migration Security.
Optimizing your cloud environment is about maximizing value over time:
- Post-migration cost optimization: The cloud offers incredible flexibility, but without careful management, costs can escalate. We continuously analyze your cloud spend, identify opportunities for savings, and implement strategies like right-sizing resources, leveraging reserved instances, and utilizing cloud-native tools for cost management. Our More info about Cloud Migration Cost Savings guide offers further details.
- Performance tuning: We fine-tune your cloud resources for optimal performance, ensuring your applications run efficiently and deliver the best possible user experience. This might involve adjusting machine types, optimizing configurations, or leveraging faster storage options.
- Right-sizing resources: Many organizations initially over-provision resources in the cloud. We help you right-size your instances and services to match actual demand, eliminating unnecessary expenses without compromising performance.
- Implementing cloud-native features: The cloud is constantly evolving. We look for opportunities to integrate cloud-native features and services that can further improve performance, add new capabilities, or improve efficiency. This could include adopting serverless architectures, containers, or managed database services.
This continuous cycle of operating and optimizing ensures that your cloud investment delivers ongoing value and adapts to your evolving business needs.
Choosing the Right Migration Strategy: The 6 R’s
With a clear inventory of your workloads and a solid understanding of your business objectives, the next step in our cloud migration phases is to determine the best strategy for each application. There’s no one-size-fits-all approach; instead, we leverage a framework often referred to as the “6 R’s” (sometimes expanded to 7 or 8 R’s by some providers) to guide these crucial decisions. Each “R” represents a distinct approach, chosen based on business drivers, technical requirements, and cost implications.
Here are the 6 R’s we consider for your cloud migration:
- Rehost (Lift and Shift)
- Replatform (Lift and Reshape)
- Refactor / Re-architect
- Repurchase (Drop and Shop)
- Retire
- Retain
Choosing the right strategy for each workload is paramount. It involves a deep dive into its dependencies, business criticality, technical debt, and long-term strategic value. Our More info about Cloud Migration Strategies provides a more in-depth look at this critical decision-making process.
Rehost (Lift and Shift)
Rehosting, often called “lift and shift,” is the process of moving applications to the cloud without significant changes to their architecture or code. It’s like moving your furniture from one house to another without buying new pieces.
- When to use it: This is typically the fastest migration path, making it ideal for large legacy migrations where the goal is to quickly scale operations in the cloud. It’s a great way to build foundational cloud operations and gain initial cloud experience.
- Benefits: Speed, minimal initial effort, and a good way to get a quick win in the cloud. Applications can then be optimized or re-architected more easily once they are already running in the cloud.
Replatform (Lift and Reshape)
Replatforming, sometimes called “lift, tinker, and shift,” involves making minor cloud optimizations to an application to achieve tangible benefits, without changing its core architecture. Think of it as upgrading your old sofa with new cushions and a slipcover—it’s still the same sofa, but it looks and feels better.
- When to use it: This strategy is suitable for workloads that can benefit from Platform-as-a-Service (PaaS) solutions, such as moving a self-managed database to a managed database service like Amazon RDS or Azure SQL Database.
- Benefits: Reduced operational overhead, improved reliability, and simplified disaster recovery, all without the high cost and effort of a full rewrite.
Refactor / Re-architect
Refactoring or Re-architecting involves reimagining how an application is built and developed, often by employing advanced cloud-native features. This is like designing and building a brand new custom piece of furniture specifically for your new home.
- When to use it: This strategy is driven by a strong business need to add new features, achieve significant scalability, improve performance, or reduce technical debt. It’s often used to break down monolithic applications into microservices or leverage serverless computing.
- Benefits: Open ups the full potential of the cloud, leading to significant agility, innovation, and long-term cost efficiency.
- Considerations: This approach has the highest initial cost and effort, requiring specialized skills and a longer timeline.
Repurchase (Drop and Shop)
Repurchasing, or “drop and shop,” means moving to a different product or solution, often a Software-as-a-Service (SaaS) offering, that better meets the business need. This is like deciding you don’t need your old filing cabinet anymore and instead switching to a cloud-based document management system.
- When to use it: Ideal when a suitable SaaS solution exists that can replace an existing application with minimal customization. Common examples include migrating from an on-premises CRM to Salesforce or an on-premises email server to Microsoft 365.
- Benefits: Eliminates infrastructure management entirely, shifts operational burden to the SaaS provider, and often provides immediate access to new features and updates.
Retire
Retiring simply means decommissioning applications that are no longer needed, used, or provide business value. It’s about decluttering your IT environment.
- When to use it: During the assessment phase, we identify applications that can be turned off. This could be redundant systems, outdated tools, or applications whose functionality has been absorbed elsewhere.
- Benefits: Reduces complexity, saves licensing and maintenance costs, and frees up resources for more valuable initiatives.
Retain
Retaining means keeping certain applications or IT portfolio portions on-premises.
- When to use it: This strategy is chosen when there’s no compelling business justification to migrate a workload to the cloud, perhaps due to specific regulatory compliance, contractual obligations, or recent hardware investments. It also applies to applications that are stable, compliant, and meet all current and future business needs.
- Considerations: These retained workloads might still be integrated into a hybrid cloud environment, potentially managed from the cloud using tools like Azure Arc, but their core infrastructure remains on-premises.
Frequently Asked Questions about Cloud Migration Phases
We understand that moving to the cloud can bring up a lot of questions. Here are some of the most common ones we encounter when discussing cloud migration phases with our clients in Florida and Texas:
What are the most common challenges during a cloud migration?
While the benefits of cloud migration are clear, the path is rarely without bumps. Our experience shows that the most common challenges include:
- Inadequate Planning: This is perhaps the biggest pitfall. Without a detailed roadmap, dependency mapping, and a clear understanding of business objectives, migrations can become chaotic.
- Unexpected Costs: Miscalculating Total Cost of Ownership (TCO), underestimating data transfer fees, or failing to optimize resources post-migration can lead to budget overruns.
- Security Gaps: The shared responsibility model in the cloud means organizations must actively manage their security posture. Neglecting identity and access management, data encryption, or compliance can expose vulnerabilities.
- Data Loss or Corruption: Poorly executed data migration strategies, especially for large volumes or complex databases, can lead to data integrity issues.
- Lack of In-House Skills: Many internal IT teams may not have the expertise required for complex cloud architectures, security configurations, or cloud-native development.
A phased approach helps mitigate these by allowing for testing, learning, and adjustment throughout the Cloud Migration Process. Each phase provides checkpoints to address issues before they escalate, ensuring a smoother transition.
How long does a cloud migration take?
The timeline for a cloud migration is highly variable, depending on several factors:
- Complexity of Workloads: Simple, standalone applications are much quicker to move than complex, interdependent enterprise systems.
- Number of Applications/Data Volume: Migrating a few applications with moderate data is vastly different from moving an entire data center with petabytes of information.
- Chosen Strategy: A “lift and shift” (rehost) approach is generally the fastest, often taking weeks for individual applications or months for larger portfolios. In contrast, a comprehensive refactoring or re-architecting effort can extend to months or even years, as it involves significant code changes and re-engineering.
- Organizational Readiness and Resources: The availability of skilled staff, executive support, and clear communication channels can significantly impact the pace of migration.
For example, a full Data Center Migration involving thousands of interdependent workloads can indeed take years. However, by starting with smaller, less critical applications, we can achieve early wins and build momentum.
What is a rollback plan and why is it essential?
A rollback plan is a carefully documented procedure to revert to the previous stable state if a migration step fails or introduces unacceptable risks. Think of it as an emergency brake for your migration project.
It is absolutely essential because:
- Minimizes Business Disruption: In the event of an unforeseen issue, a well-defined rollback plan allows for a quick return to a functional state, limiting downtime and impact on operations.
- Prevents Data Loss: It ensures that if data transfer or application configuration goes awry, you can restore your systems to a point before the failure occurred, protecting critical information.
- Builds Confidence: Knowing there’s a safety net provides confidence to the migration team and stakeholders, encouraging bolder, yet still calculated, moves.
- Reduces Risk: It acts as a critical risk mitigation strategy during the inherently complex and critical migration execution phase. We always define clear rollback criteria and thoroughly test these procedures before any major migration step.
Conclusion
Navigating the complexities of cloud adoption can be daunting, but by understanding and diligently following the cloud migration phases, organizations can transform potential chaos into a strategic advantage. We’ve explored how a structured, 5-phase approach—Prepare, Plan, Migrate, Operate, and Optimize—coupled with thoughtful consideration of migration strategies like the 6 R’s, minimizes risk, reduces downtime, and maximizes your return on investment.
Cloud migration isn’t a one-time project; it’s a continuous journey of change and improvement. It’s about establishing a modern operating model that supports ongoing modernization and innovation, driving sustained business value.
The good news is that you don’t have to start on this journey alone. As your trusted partner, Cyber Command brings decades of experience in guiding businesses through each of these critical cloud migration phases. Our proactive, 24/7/365 U.S.-based support, transparent pricing, and deep expertise ensure that your transition to the cloud is smooth, secure, and successful. We’re here to act as an extension of your business, helping you leverage the full power of the cloud.
Ready to open up the benefits of a well-executed cloud migration for your business in Florida or Texas? Partner with us for your Cloud Migration today.


