Unlock the Power of the Cloud: Essential Computing Solutions

Why Cloud Computing Solutions Are Changing Modern Business
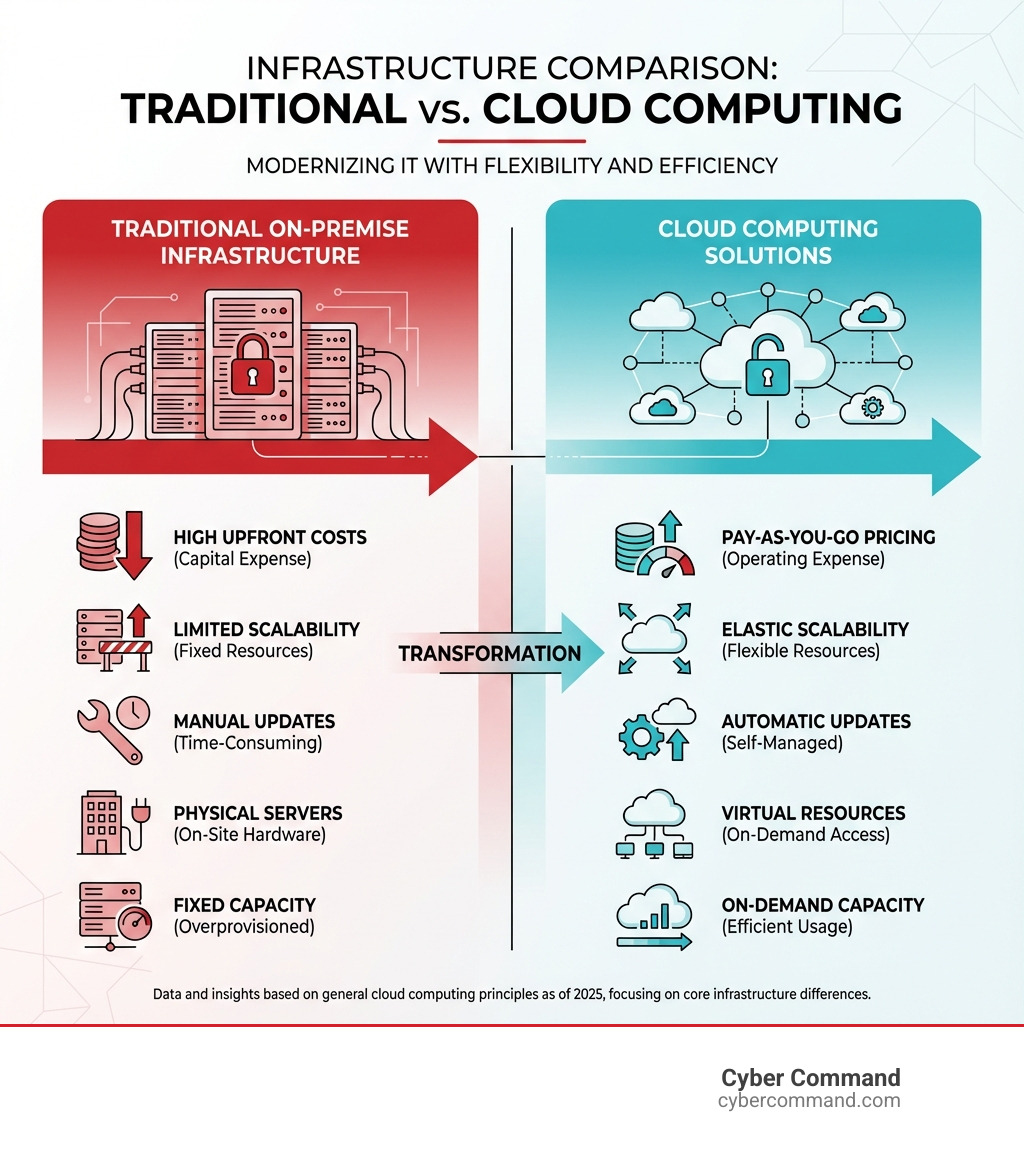
Cloud computing solutions deliver IT resources—like servers, storage, databases, and software—over the internet, eliminating the need for costly on-site hardware and providing access to powerful tools on demand.
What You Need to Know About Cloud Computing Solutions:
- On-Demand Access: Get computing resources whenever you need them, from anywhere with an internet connection
- Pay-As-You-Go Pricing: Only pay for what you use, turning large capital expenses into predictable operating costs
- Three Main Service Models: Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), Platform as a Service (PaaS), and Software as a Service (SaaS)
- Deployment Options: Choose between public cloud (shared resources), private cloud (dedicated resources), or hybrid cloud (combination of both)
- Key Benefits: Lower costs, faster deployment, automatic scaling, improved disaster recovery, and improved security
Before the cloud, businesses faced huge upfront investments in expensive data centers with physical servers and storage arrays, leading to high maintenance costs and limited flexibility. Cloud computing flips that model.
Instead of buying and managing hardware, you rent computing power from providers like Amazon Web Services, Microsoft Azure, or Google Cloud. Resources are available in minutes, capacity scales automatically, and you eliminate the capital expense of running an onsite datacenter.
Most cloud services operate on a self-service, on-demand basis. This speed enables innovation that simply wasn’t possible before, allowing teams to experiment with new ideas and deploy applications at a pace that traditional infrastructure could never support.
The cloud also makes data backup and disaster recovery dramatically easier and less expensive. Your data is automatically mirrored across multiple redundant sites on the provider’s network. If something goes wrong at one location, your business keeps running.
For growing businesses, this shift matters enormously. You’re no longer constrained by the physical limits of your own infrastructure. You can focus resources on your core business instead of managing IT hardware. And you gain access to enterprise-grade technology—from machine learning platforms to advanced analytics tools—that would be prohibitively expensive to build yourself.
I’m Reade Taylor, founder and CEO of Cyber Command, and I’ve spent my career helping businesses steer complex technology decisions, from engineering enterprise security systems at a major tech corporation to building secure, cloud-based infrastructure for organizations today. Through years of implementing cloud computing solutions for clients, I’ve seen how the right approach transforms IT from a cost center into a competitive advantage.
What is Cloud Computing and Why Does It Matter?
At its core, cloud computing is about delivering computing services—including servers, storage, databases, networking, software, analytics, and intelligence—over the internet, or “the cloud.” Think of it as accessing IT resources on demand, over the Internet, and on a pay-per-use basis. This means your company doesn’t need to purchase, install, operate, or upgrade hardware for physical data centers. Instead, we can rent resources as needed from cloud service providers.
This model is a game-changer because it eliminates the capital expense of buying hardware and software and setting up and running onsite datacenters. Instead, cloud providers typically employ a pay-as-you-go pricing model, which means that organizations only pay for the cloud services that they use. This helps companies significantly lower operating costs, run infrastructure more efficiently, and scale as business needs change.
The cloud also empowers faster innovation. By providing easy access to a broad range of technologies, from basic compute and storage to advanced services like IoT and machine learning, cloud resources can be provisioned in minutes. This rapid deployment allows for significantly faster idea-to-implementation cycles, accelerating your business’s ability to develop and experiment with new ideas. For a deeper dive into the advantages, explore the Benefits of Moving to the Cloud.
The Core Benefits for Your Business
The shift to cloud computing isn’t just a trend; it’s a strategic move that offers profound advantages for businesses of all sizes, especially in competitive markets like Florida and Texas.
- Cost Savings: Reduce capital expenditure by eliminating the need for expensive hardware and data center upkeep. You pay only for what you use, converting large upfront costs into predictable operational expenses and freeing up resources for growth.
- Speed and Agility: Provision vast computing resources in minutes with self-service, on-demand access. This agility allows your business to respond quickly to market changes, launch products faster, and experiment without large upfront investments.
- Scalability and Elasticity: Automatically scale resources up or down to meet fluctuating demand. Unlike traditional infrastructure, which can take weeks to scale, the cloud’s elasticity ensures optimal performance without over-provisioning.
- Increased Productivity: Free your IT teams from infrastructure management tasks like server patching. By abstracting these complexities, the cloud allows them to focus on high-value activities that drive business growth and enables seamless collaboration from anywhere.
- Performance and Reliability: Leverage massive global networks of secure data centers for high performance and reliability. Data is mirrored across redundant sites, making disaster recovery and business continuity easier and less expensive, which means less downtime for your critical applications. For comprehensive strategies, check out our Cloud Disaster Recovery Options Complete Guide.
Real-World Use Cases
Cloud computing isn’t just for tech giants; it’s powering everyday operations and groundbreaking innovations for businesses across industries. Here are some real-world applications we see our clients leveraging in Florida and Texas:
- Data Backup and Recovery: Use cloud storage for robust, cost-effective data backup instead of physical tapes or local drives. In case of a local disaster, data can be quickly restored from the cloud to ensure business continuity.
- Application Development and Testing: Accelerate the development lifecycle by allowing developers to spin up and tear down entire dev/test environments in minutes. This reduces costs and enables rapid iteration, with providers like Google Cloud offering pre-built templates for quick deployment.
- Big Data Analytics: Use the cloud’s scalable compute and storage for big data processing. This enables businesses to analyze vast datasets and make smarter, data-driven decisions using services like Google Cloud’s BigQuery for analytics at scale.
- Software Delivery (SaaS): Access ready-to-use applications like CRM systems (e.g., Salesforce), email, or collaboration tools over the internet. The SaaS model eliminates local installation and maintenance, offering ultimate convenience and accessibility.
- IoT Platforms: The cloud provides the necessary infrastructure to ingest, process, and analyze massive amounts of data from Internet of Things (IoT) devices. This enables smart applications and services, with platforms like Azure IoT offering secure, scalable solutions.
- Machine Learning Models: Build AI-driven applications without investing in specialized hardware. The cloud offers powerful, scalable resources for training and deploying complex machine learning models, enabling everything from predictive analytics to personalized customer experiences.
Understanding the Core Cloud Computing Solutions
When we talk about cloud computing solutions, it’s helpful to understand the different layers of service and deployment models available. Imagine building a house: you can buy the land and build everything yourself, buy a pre-built house, or rent an apartment. Cloud computing offers similar choices in how much control you want over your IT environment.
The level of control you have is often tied to the “shared responsibility model” in cloud computing. This model clarifies what the cloud provider is responsible for (e.g., the physical infrastructure, security of the cloud) and what you, the customer, are responsible for (e.g., your data, applications, security in the cloud). Understanding this division is crucial for effective cloud management. To Learn basic cloud concepts, you can explore various online modules.
The “As-a-Service” Models: IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS
These three models represent the most common ways that cloud computing solutions are delivered, each offering a different level of management and flexibility.

-
Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS):
- What it is: The most basic cloud service model, IaaS provides fundamental computing resources like virtual servers, storage, and networks over the internet. It’s like renting the building blocks of IT infrastructure without buying or managing the physical hardware.
- Your responsibility: You manage the operating systems, applications, and data, while the provider manages the underlying physical infrastructure.
- Use cases: Ideal for hosting websites, running custom applications, or for development and testing environments where you need high-level control. Major providers include AWS, Microsoft Azure, and Google Compute Engine.
- Why it matters: IaaS offers maximum flexibility, allowing you to build and customize virtual infrastructure without the capital expense of physical hardware.
-
Platform as a Service (PaaS):
- What it is: PaaS provides a complete development and deployment environment in the cloud, abstracting away the underlying infrastructure. It allows developers to focus on building, testing, and deploying applications.
- Your responsibility: You manage your applications and data, while the provider manages everything else, including operating systems, runtime, and servers.
- Use cases: Perfect for developers building custom web or mobile apps. Examples include Google App Engine, Heroku, and AWS Elastic Beanstalk.
- Why it matters: PaaS accelerates application development, allowing teams to innovate and bring products to market faster by focusing on code, not infrastructure.
-
Software as a Service (SaaS):
- What it is: SaaS delivers ready-to-use software applications over the internet, usually on a subscription basis. Users simply access the application online without any local installation.
- Your responsibility: You just use the software. The provider manages everything from the application down to the physical hardware.
- Use cases: Common examples include email (Google Workspace, Microsoft 365), CRM software (Salesforce), and collaboration tools (Notion, Confluence).
- Why it matters: SaaS offers plug-and-play convenience, eliminating the need for software installation, maintenance, or updates, so your team can be productive immediately.
These models offer different degrees of control and management, allowing us to select the approach that best fits our specific needs and budget. For a broader understanding of various Cloud Services, we provide extensive resources.
Finding Your Fit: Public, Private, and Hybrid Clouds
Beyond the service models, cloud computing solutions are also deployed in different environments, each with its own advantages.

-
Public Cloud:
- What it is: Owned and operated by third-party providers like AWS, Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud, public clouds deliver computing resources over the internet. Resources are shared among multiple organizations, but your data remains logically separate and secure.
- Characteristics: Offers massive scalability, high reliability, and a pay-as-you-go pricing model.
- Use cases: Ideal for most businesses due to its cost-effectiveness and scalability, especially for web applications and development environments.
-
Private Cloud:
- What it is: A private cloud consists of computing resources used exclusively by a single organization. It can be located on-premises or hosted by a third-party provider.
- Characteristics: Provides greater control, security, and privacy since resources are not shared. It’s often chosen for sensitive data or applications with strict regulatory requirements.
- Use cases: Common for government, finance, and healthcare organizations that require stringent security and compliance.
-
Hybrid Cloud:
- What it is: A hybrid cloud combines public and private clouds, allowing data and applications to be shared between them. This model offers the best of both worlds.
- Characteristics: Provides great flexibility, allowing you to run sensitive applications on a private cloud while leveraging the public cloud for less-sensitive, high-traffic workloads. Data and applications can move seamlessly between environments.
- Use cases: Often used to manage fluctuating demand (cloud bursting), for disaster recovery, or to gradually migrate legacy applications. It’s a strategic approach that balances flexibility, cost, and control. To learn more about how to steer this, consider developing a robust Cloud Migration Strategy.
Choosing the right deployment model depends on your specific business needs, regulatory compliance requirements, and budget. Many businesses are finding that a hybrid approach offers the most balanced and flexible path forward.
How to Choose a Partner and Ensure Security
Selecting the right cloud service provider is a critical decision that can significantly impact your business’s operations, security posture, and bottom line. It’s not just about finding the cheapest option; it’s about finding a partner that aligns with your strategic goals and can deliver the reliability, performance, and security your business demands.
When evaluating providers, we guide our clients through a comprehensive assessment, looking beyond just the flashy features. We dig into their service level agreements (SLAs), which are contractual agreements guaranteeing uptime, performance, and support. We also consider how easily their services integrate with your existing systems and what level of technical support they offer. Data governance, which dictates how your data is managed, stored, and protected, is another key factor to prevent vendor lock-in and ensure compliance.
| Feature / Factor | Description |
|---|---|
| Security | Evaluate the provider’s security measures, including encryption, access controls, threat detection, and compliance certifications. Does it meet industry best practices and your regulatory needs? |
| Compliance | Crucial for regulated industries. Does the provider offer certifications like HIPAA, HITECH, SOC 2, or SOC 3? This ensures they meet specific data protection and privacy standards. |
| SLA (Uptime) | Review the Service Level Agreement to understand guaranteed uptime, performance metrics, and recourse for service disruptions. A strong SLA is a promise of reliability. |
| Support | Assess the availability and quality of technical support. Is it 24/7? What are the response times? Do they offer dedicated support for critical issues? |
| Pricing Model | Understand the pay-as-you-go structure, potential hidden costs, and options for cost optimization. Can you easily predict and manage your cloud spend? |
| Integration | How well does the cloud platform integrate with your existing applications, systems, and tools? Seamless integration minimizes disruption and maximizes efficiency. |
| Scalability | Can the provider easily scale resources up or down to meet fluctuating business demands without performance degradation? |
| Data Governance | Understand how the provider manages your data, including data residency, backup policies, and disaster recovery options. This is vital for data control and compliance. |
| Vendor Lock-in | Consider the ease of migrating your data and applications to another provider if needed. Strong portability options reduce the risk of being tied to a single vendor. |
Key Considerations for Your Cloud Computing Solutions
When we help businesses in Florida and Texas select their cloud computing solutions, we focus on several key areas to ensure a perfect fit:
- Business Needs Assessment: First, we identify your specific business requirements: the problems you’re solving, the applications you’re moving, and your performance demands. This understanding is the foundation of a successful cloud strategy.
- Compatibility and Integration: We evaluate how well a provider’s services integrate with your existing IT infrastructure and workflows. Seamless integration is key to minimizing disruption and maximizing efficiency.
- Reliability and Performance: Downtime is costly. We assess a provider’s track record for uptime and network performance. A strong Service Level Agreement (SLA) with guarantees for uptime is non-negotiable. For example, some providers offer a 100% uptime SLA, which is a strong indicator of reliability.
- Compliance Certifications (HIPAA, SOC 2, etc.): For many industries, regulatory compliance is paramount. If you handle sensitive data (like healthcare information under HIPAA), selecting a provider with the necessary certifications is critical. Look for providers that offer HIPAA, HITECH, SOC 2, and SOC 3 certifications to meet strict compliance needs. Our expertise in Cloud Migration Security also guides clients through these crucial decisions.
Security in the Cloud: Risks and Rewards
Cloud security is a topic we take very seriously at Cyber Command. While cloud providers offer robust security measures, understand that security in the cloud is a shared responsibility.
- Shared Responsibility Model: This model clarifies security duties: the provider secures the cloud itself (physical infrastructure), while you secure what’s in the cloud (your data, applications, and configurations). Understanding this distinction is vital.
- Benefits of Provider Security: Cloud providers invest heavily in security, offering advanced encryption, physical data center security, and threat detection systems that often exceed what a single business can afford. This strengthens your overall security posture.
- Common Threats: Cloud environments are not immune to threats. Common risks include misconfigurations (the #1 cause of cloud breaches), weak access controls, and poor credential management. A recent example showed one MSP facing three Microsoft 365 compromises in 72 hours—a stark reminder that vigilance is key.
- Access Controls and Data Encryption: Implementing strong access controls (like multi-factor authentication) and ensuring data is encrypted both at rest and in transit are fundamental steps we help clients take to secure their cloud computing solutions.
The Future of the Cloud and Your Workforce
The cloud is a dynamic landscape, constantly evolving with new technologies that redefine what’s possible for businesses. This digital change is driving unprecedented business modernization, and staying ahead means understanding these shifts. Our focus at Cyber Command is not just on implementing current cloud computing solutions, but also preparing our clients for the future through strategic planning and proactive adoption of emerging technologies. This often involves leveraging Cloud Automation to streamline operations and improve efficiency.
The Future of Cloud Computing Solutions and Innovation
The cloud isn’t standing still; it’s rapidly integrating with cutting-edge technologies:
- Serverless Computing: This model lets you run applications without managing servers. The provider handles all infrastructure provisioning and scaling, and you only pay for the compute time you use. It’s highly efficient and event-driven, using resources only when a specific function is triggered.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML): Cloud platforms are integrating powerful AI and ML services, giving businesses easy access to tools for predictive analytics and natural language processing without investing in specialized hardware or AI experts. Providers like Google Cloud and Microsoft Azure are leading this charge, offering services to build and scale AI applications.
- Edge Computing: Edge computing processes data closer to its source, like an IoT device. This reduces latency and bandwidth usage, enabling faster insights and more responsive applications in sectors like manufacturing and logistics.
- Multi-cloud Strategies: Many businesses now use a multi-cloud strategy, leveraging services from multiple providers to avoid vendor lock-in, mitigate risk, and use the best tool for each job. This approach increases flexibility but requires careful management, where Cloud Infrastructure Automation becomes indispensable.
Essential Skills and Roles in the Cloud-First Era
The demand for cloud expertise is soaring, creating new and exciting career opportunities. While it might seem intimidating, general cloud computing does not always require deep technical IT experience. Many roles leverage existing IT knowledge and apply it to the cloud context.
Here are some key job roles emerging in the cloud computing industry:
- Cloud Architect: Designs and oversees an organization’s cloud computing strategy, ensuring the infrastructure meets business needs for scalability, security, and performance.
- Cloud Engineer: Builds, deploys, and maintains cloud applications and services on platforms like AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud, often using automation and infrastructure as code.
- DevOps Engineer: Automates and streamlines software delivery pipelines, bridging the gap between development and operations to enable continuous integration and delivery (CI/CD) in the cloud.
- Security Engineer (Cloud): Specializes in protecting cloud environments by identifying risks, implementing security controls, and monitoring for threats to safeguard data and applications.
- Cloud Consultant: Advises businesses on cloud strategy, migration, and optimization. They help organizations steer the complexities of cloud adoption, often working with IT service providers like us.
- Data Engineer/Scientist: Designs and manages data pipelines in the cloud, using cloud-based AI/ML tools to extract valuable insights from large datasets.
Required skills often include familiarity with major cloud platforms, networking, security, and automation. The good news is that many existing IT skills are transferable, and a basic understanding of computing concepts provides a solid foundation for learning cloud technologies.
Conclusion
We’ve explored the expansive world of cloud computing solutions, from their fundamental definitions to their profound impact on modern business. We’ve seen how the cloud transforms IT from a capital-intensive burden into a flexible, scalable, and cost-effective engine for innovation. By understanding the different service models (IaaS, PaaS, SaaS) and deployment options (public, private, hybrid), businesses can tailor their cloud strategy to their unique needs.
The core benefits are undeniable: significant cost savings, unparalleled speed and agility, elastic scalability to meet any demand, increased productivity, and robust performance with built-in reliability and disaster recovery capabilities. From streamlining data backups to powering advanced AI and machine learning, cloud computing is not just a technology; it’s a strategic business advantage.
However, navigating this complex landscape and ensuring robust security requires a clear strategy and, often, the expertise of a trusted IT partner. Understanding the shared responsibility model for security and carefully considering compliance, integration, and support are paramount when choosing a cloud service provider.
At Cyber Command, we are deeply committed to helping businesses in Winter Springs, Orlando, Jacksonville, Tampa Bay, Central Florida, and Plano, Texas, harness the full potential of these transformative technologies. We believe that with the right cloud computing solutions and expert guidance, your business can achieve unprecedented levels of efficiency, innovation, and growth.
Ready to open up the power of the cloud for your business? Let us help you design, implement, and manage the perfect cloud strategy. Get expert help with our Managed IT Services and let’s build your future, today.

