Everything You Need to Know About the Department of Transport
Discover key insights on the Department of Transport, covering services, state-specific info, and FAQs. Essential read for all travelers.
Discover key insights on the Department of Transport, covering services, state-specific info, and FAQs. Essential read for all travelers.
In an era where commerce and conversation have transitioned to the digital realm, small businesses face a complex new world fraught with cyber threats. No longer exclusive to colossal entities, cyber-attacks have become a daily battle for small businesses striving to safeguard their operations. Among many digital dangers, one particular threat looms and strikes more frequently, compromising sensitive data, extorting finances, and eroding customer trust.
But what is this prevalent menace, and why are small businesses so vulnerable to its crippling grasp? What measures can businesses implement to defend themselves against this malicious force? This article aims to comprehensively answer these questions and equip small business owners with valuable knowledge and resources to protect their enterprises. Continue reading to gain valuable insights!

The cyber threat landscape for small businesses is vast and intimidating. According to the Verizon 2022 Data Breach Investigations Report, 43% of cyber attacks target small to medium-sized businesses. This disproportionate focus is due to the typically lower defenses in small enterprises, which make them attractive targets for cybercriminals. Common attacks include phishing, where fraudulent communications from reputable sources aim to collect sensitive data. Ransomware also poses a significant threat; attackers encrypt critical data and demand payment for its release.
In the first half of 2021, the U.S. Treasury’s Financial Crimes Enforcement Network identified $590 million in suspicious activity linked to ransomware. Additionally, malware infections can disrupt operations and lead to data breaches. These issues can be catastrophic. The National Cyber Security Alliance reports that 60% of small companies cannot sustain their businesses over six months following a brute force attack. Given this barrage of threats, small businesses must take proactive and robust cybersecurity measures. Elevating digital defenses to fortify against this ubiquitous and ever-evolving threat landscape is crucial.

The most common cyber attacks small businesses encounter are multifaceted and continuously evolving, requiring constant vigilance. Below are some of the most prevalent types of cyber attacks small businesses face:
As a small business owner, you are likely familiar with “phishing.” However, do you know just how prevalent and dangerous this type of cyber attack can be? Phishing attacks occur when hackers send fraudulent emails that appear to come from reputable sources, such as banks or government agencies. These emails often contain urgent or enticing language, prompting recipients to click on malicious links or attachments that can infect their devices with malware. For example, a phishing attack email might claim to be from your bank, warning you of suspicious activity on your account and urging you to click on a link to verify your login credentials.
However, this link leads to a fake website that collects your personal information, leaving you vulnerable to identity theft and financial fraud. Phishing attacks are widespread and can have devastating consequences for small businesses, so educating yourself and your employees about how to spot and avoid them is crucial. End users should be cautious of emails that request personal information or legitimate service requests that require urgent action, even if they appear to come from trusted sources. Regular cybersecurity training and implementing email filters can also be effective in mitigating the risk of spear phishing attacks on small businesses.
Ransomware is malicious software that encrypts your data and holds it for ransom, demanding payment from the victim in exchange for its release. This cyber attack has become increasingly prevalent in recent years, affecting businesses of all sizes and industries. One notable example is the 2017 WannaCry attack that targeted thousands of organizations worldwide, including small businesses and hospitals, causing widespread disruption. The attack encrypted critical data files and demanded a ransom of $300 in Bitcoin for their release.
While many large organizations have backups or the means to pay the ransom, smaller businesses often lack these resources, making them more susceptible to losing valuable data or suffering financial losses. The consequences of a successful ransomware attack can be devastating for small businesses, making it crucial to protect against this threat proactively. Implementing data backups and regularly updating software can help mitigate the risk of ransomware attacks. Additionally, investing in cybersecurity insurance can provide financial protection in case of a DDOS attack.
Malware, short for ‘malicious software,’ refers to any program or file that is intentionally created to cause harm to a computer, network, client, or server. Imagine yourself as a small business owner. You innocently click on a seemingly harmless link or download what appears to be an important update. Suddenly, your screen freezes, and before you know it, your computer systems are compromised with SQL injection attacks that can spy on your transactions, steal customer information, disrupt your services, or even exploit your business’s computing power for malicious purposes.
For example, Trojan Horse, a type of malware disguised as legitimate software, can provide cybercriminals with a backdoor into your system, granting them unrestricted access to your business’s most sensitive data. Malware can infiltrate your system through various channels, such as downloaded software, compromised websites, or infected email attachments. The covert nature of these programs makes them particularly dangerous, as they can operate undetected for long periods, causing significant and irreversible damage. Implementing antivirus and anti-malware software and regularly scanning your system can help prevent malware attacks on small businesses.
Denial-of-Service (DoS) and Distributed Denial-of-Service (DDoS) attacks have become notorious for their ability to overwhelm the victim’s systems with a flood of traffic. These assaults aim to render a website or online service inoperable, effectively denying service to legitimate users. Small businesses may struggle to mitigate such attacks due to limited cybersecurity resources.
For instance, an attacker might target a small online retailer during a peak shopping period, not only causing immediate loss of sales but also damaging the retailer’s reputation for reliability. To guard against these attacks, businesses can implement network security measures, such as firewalls and intrusion detection systems, and develop an incident response plan to restore services quickly during an SQL injection attack.
Man-in-the-middle (MitM) attacks are cyber-attacks where the attacker intercepts and manipulates communication between two parties without either party being aware. This allows the attacker to eavesdrop on sensitive information, such as login credentials or financial transactions, and potentially alter or sabotage the communication. As a small business owner, you may think communicating with third-party vendors or clients is secure, but MitM attacks can compromise this trust.
For example, an attacker could use a Wi-Fi hotspot at a coffee shop to intercept your data while you are conducting business on your laptop, giving them access to valuable information and potentially causing financial harm to your business. To protect against MitM attacks, businesses should implement encryption protocols for communication and avoid using public Wi-Fi for sensitive tasks. Regular security audits can also help identify and prevent potential vulnerabilities in the system that MitM attackers could exploit. As a small business owner, staying vigilant and taking proactive measures to protect your business from these cyber threats is essential.
Social engineering is a manipulation technique cybercriminals use to trick individuals into divulging sensitive information or performing actions that compromise security. These attacks rely on human psychology and exploit people’s trust, fear, and other emotions to gain access to systems or data. You may think your employees would never fall for such tactics as a small business owner, but social engineering attacks can be highly deceptive and convincing.
For instance, an attacker might impersonate a trusted source, such as a bank representative or IT support, to request login credentials or other sensitive information. Alternatively, they may use social media platforms to gather personal information about employees and use it to gain access to the business’s systems. Training employees to recognize and respond to social engineering tactics, such as phishing emails and phone scams, can help prevent these attacks. It is crucial to establish strict protocols for sharing sensitive information within the company and regularly review and update them to avoid potential social engineering threats.

Small businesses may face additional vulnerabilities that make them attractive targets for cyber attacks. Here are some common vulnerabilities that small businesses must address to protect their systems and data:
Small businesses often lack the proper cybersecurity policies to protect their systems and data from potential password attacks. Without clear guidelines, employees may not know how to handle sensitive information, leaving them vulnerable to social engineering tactics or inadvertently causing a data breach. For example, if you run a small accounting firm and have multiple employees handling clients’ financial information on different devices.
In that case, it is crucial to establish a strict policy on how and where this information can be accessed and shared to prevent hackers who steal data using brute force attacks. Cybersecurity policies should also include guidelines for employee training, incident response plans, and regular security audits to ensure the company’s overall security posture. By implementing comprehensive cybersecurity policies, small businesses can mitigate potential vulnerabilities and reduce the risk of XSS attacks.
Running on outdated software can open the door to a litany of security vulnerabilities, particularly for small businesses that may not have continuous access to an IT support team. Neglecting to update your software can provide cybercriminals with easy access to your systems through security loopholes that have since been patched in newer versions. If you’re running a local boutique that relies on a point-of-sale (POS) system to process customer transactions.
If your software is outdated, a known vulnerability might allow a hacker to infiltrate your network and siphon off customer credit card information, leading to a devastating loss of customer trust and potentially ruinous financial penalties. Therefore, it’s not just advisable but imperative to ensure that all of your software, from application suites to operating systems, is updated with the latest security patches. Regularly scheduled updates and a robust cybersecurity strategy can fortify your business against such exploits.
Inadequate password protection poses a significant vulnerability for small businesses. Weak or reused passwords can be easily compromised, granting unauthorized access to sensitive business systems. Many breaches occur due to passwords that are either too simplistic, widely used across multiple accounts, or unchanged for extended periods. For instance, insider threats can effortlessly breach these accounts if employees utilize default or easily guessable passwords, such as “password123,” for their workstations or business applications.
To enhance security, small businesses should enforce robust password policies. These policies should require complex combinations of letters, numbers, and symbols. Additionally, implementing multi-factor authentication adds an extra layer of defense. Regular password changes should be encouraged, and password management tools to securely store and generate strong, unique passwords for each account are highly recommended.
Unsecured remote access constitutes a significant vulnerability for small businesses, especially with the rise of remote work environments. When remote access to a business’s network is not properly secured, it can be a gateway for cybercriminals to enter and exploit the system. For instance, a small marketing firm with employees from different locations may use malicious code protocols to access company network resources.
Without proper security measures, such as VPNs with strong encryption or secure tunneling protocols, cross-site scripting attackers could intercept the firm’s data. Implementing stringent security measures for remote login procedures and educating staff on the dangers of unsecured remote connections are crucial to safeguarding a business’s digital assets.
Outdated or misconfigured firewalls pose a significant risk to small businesses. A firewall is the first defense against external threats, but its effectiveness diminishes if it’s not regularly updated or properly configured. For instance, consider a small legal practice that installs a firewall to safeguard its network, housing sensitive case files and client information.
Their network becomes vulnerable to unauthorized access and potential data breaches without appropriate configuration to manage permitted traffic types or close unused ports. To enhance network security, it is crucial to regularly review firewall rules, ensure the latest firmware updates, and engage a professional to configure these settings. This is an essential step in fortifying the network security of small businesses.
Employees can unknowingly become the weakest link in a small business’s cybersecurity efforts. Without adequate training or awareness of cyber threats, they may unknowingly fall prey to social engineering tactics that compromise company data. For example, employees could receive an email posing as a trusted source requesting sensitive computer system information, such as login credentials, which cybercriminals can use to gain unauthorized access.
Small businesses should invest in regular employee training and awareness programs to educate staff about potential threats, how to identify them, and proper protocols for handling sensitive information. Implementation of simulated phishing exercises can also help employees recognize and avoid fraudulent emails. Small businesses can significantly reduce the risk of successful eavesdropping attacks by equipping employees with the necessary knowledge and skills.
Third-party vendors often provide essential services to small businesses but can also introduce new vulnerabilities if their cybersecurity measures are not stringent. A vendor’s exploit vulnerabilities can serve as a conduit through which cybercriminals can access a business’s sensitive data. For example, a small business might outsource its payroll processing to an external company; if that company suffers a data breach, employees’ personal information could be exposed, leading to serious privacy violations and potential financial loss.
Small businesses must conduct thorough security assessments of their vendors and stipulate cybersecurity requirements in their service agreements to protect themselves. Ensuring that third-party vendors have robust security policies and practices in place, such as regular audits and compliance with industry-standard cybersecurity frameworks, is imperative. Additionally, businesses should have an incident response plan that includes protocols for addressing breaches from third-party vendors.
Small businesses face a multifaceted cybersecurity landscape that requires vigilant and comprehensive strategies. From ensuring up-to-date systems and software to enforcing strong password policies and securing remote access, each step is critical in protecting valuable data and resources. Furthermore, the importance of employee education and the need to thoroughly vet third-party vendors cannot be overstated. By recognizing and addressing these common vulnerabilities, small businesses can fortify their defenses and establish a resilient cybersecurity posture that safeguards their business operations, reputation, and the trust of their clients.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) has emerged as a game-changer in business in today’s rapidly evolving digital landscape. This revolutionary technology is no longer a futuristic concept confined to the realms of sci-fi; instead, it is a tangible reality that is reshaping the bedrock of various industries, from healthcare and finance to retail and everything in between. By leveraging AI, businesses are unlocking unprecedented efficiency, accuracy, and productivity levels, creating a seismic shift in traditional business operations.
This powerful tool is revolutionizing decision-making processes, customer service, predictive analysis, and much more, ushering in a new era of business intelligence. But how exactly is AI being harnessed within the business context? What are its applications, implications, and potential pitfalls? In this article, we delve into the heart of these questions, unpacking the role and scope of AI in modern business. So, without further ado, let’s embark on this journey of discovery and explore how AI influences businesses today and sets the stage for tomorrow’s businesses. Continue reading to reveal the transformative power of AI in the world of business.

The advent and proliferation of AI in the business world represent a significant shift in how organizations operate and strategize. At the forefront of this transformation is the ability of AI to process vast amounts of data quickly and accurately, enabling businesses to make more informed decisions, optimize operations, and provide personalized customer experiences. For example, in the retail industry, machine learning algorithms can analyze customer data, predict future buying patterns, and personalize product recommendations based on individual preferences and browsing history. This level of process automation personalization enhances the customer experience and increases the likelihood of sales and customer loyalty.
In the healthcare industry, AI is revolutionizing medical practices. It can assist with medical diagnoses by analyzing patient data and providing insights to healthcare professionals. AI also plays a crucial role in drug development, enabling researchers to analyze large datasets and identify potential targets for new treatments. Additionally, AI tools can streamline patient care by automating administrative tasks, ensuring accurate record-keeping, and improving communication between healthcare providers. AI also automates routine tasks such as data science and analysis. By automating these processes, AI saves time and reduces the risk of human error, allowing employees to focus on more complex and value-added tasks.

This tool plays numerous roles in decision-making processes. Here are some of them, showcasing the diverse ways in which AI can contribute:
Predictive analytics, a prominent application of AI, leverages advanced statistical algorithms and machine learning techniques to analyze vast amounts of historical data. By navigating through this unstructured data, it can detect intricate patterns and trends that the human eye might easily overlook. This enables business benefits, enabling them to gain insightful forecasts about future events equipping them to make proactive, data-driven decisions and stay one step ahead of the competition.
For example, if you own an online retail store. With predictive analytics, you can anticipate future demand for products and services, allowing you to optimize your inventory management. By stocking up on popular items ahead of time, you can ensure timely delivery and improve customer satisfaction. Additionally, predictive analytics can help you identify potential upselling or cross-selling opportunities, enhancing your overall sales strategy.
AI has proven instrumental in streamlining businesses’ processes, automating routine tasks, and enabling teams to focus on more complex and value-adding activities. One prime example is the emergence of business leaders who integrate AI chatbots. These sophisticated computer programs are designed to simulate human conversation and are increasingly used in customer service departments. Instead of having a human operator answer repetitive and common questions, these chatbots can efficiently handle such queries, providing instant and accurate responses.
As a result, response times are significantly reduced, leading to increased customer satisfaction. The deployment of chatbots allows customer human resources to allocate their time and expertise toward handling more complex inquiries, thereby boosting overall productivity. For example, if you own a software company, implementing chatbots can effectively troubleshoot common technical issues, freeing up the team’s valuable time to concentrate on developing new products or innovative features. Integrating AI-powered chatbots into business operations signifies a transformative shift towards more efficient and customer-centric service delivery.
The remarkable ability to harness vast volumes of data has unlocked unprecedented opportunities for personalization, revolutionizing the customer experience across the board. By leveraging this advanced technology, business processes can now effortlessly track and analyze intricate details of customer behavior, preferences, and purchasing patterns in real-time. This invaluable insight allows for delivering highly personalized customer experiences that foster engagement, loyalty, and retention and exceed expectations.
For example, if you own a fitness app empowered by AI. With access to user data, this cutting-edge technology can go beyond the surface, diving deep into individual needs and goals. Through sophisticated analysis, AI can provide tailored workout plans and personalized nutrition advice, ensuring every user receives a customized and valuable experience. This level of personalization not only enhances user satisfaction but also significantly increases the likelihood of continued app usage.
This tool can be a game-changer in risk assessment and management, offering predictive accuracy and strategic insight that surpasses traditional methods. AI can efficiently sift through massive data sets through its advanced algorithms and machine-learning capabilities, uncovering subtle patterns, correlations, and anomalies that may signify potential risks or threats. This empowers businesses with a comprehensive and nuanced understanding of risk factors, enabling them to implement mitigation strategies and safeguard their operations proactively.
For example, deep learning AI can be crucial in the financial sector if you own an industry highly susceptible to fraud and cyber threats. By continuously monitoring transactions, AI can detect unusual activity or deviations from typical behavioral patterns, promptly flagging potential instances of fraud for further investigation. This reduces the likelihood of substantial financial losses and enhances reputation management, as customers tend to trust institutions that prioritize and proactively address security.
Resource allocation and optimization capabilities change how businesses manage their resources, ensuring they are used efficiently and cost-effectively. AI algorithms can analyze vast amounts of data from various sources in real-time, enabling businesses to make precise and timely decisions regarding resource allocation. This reduces wastage and enhances efficiency, leading to improved productivity and profitability. AI can continuously improve these decisions through machine learning by learning from past data, adapting to changing conditions, and predicting future trends. AI can thereby not only improve current resource management but also help businesses to plan for the future.
For example, AI can significantly optimize your production process if you run a manufacturing plant. With AI systems, you can predict machine failures before they happen by analyzing patterns and identifying anomalies in operational data, allowing you to perform preventive maintenance and avoid costly downtime. AI can also optimize your supply chain by predicting future demand and adjusting inventory and logistics accordingly. This ensures that you always have enough stock to meet demand without overstocking and increases the efficiency of your logistics by choosing the best routes and modes of transportation. AI capabilities can also help in labor scheduling, ensuring that you have the right number of employees at the right times, thereby reducing labor costs and increasing productivity. AI can play a pivotal role in resource allocation and optimization through these and other functions, helping businesses be more efficient, competitive, and sustainable.

When it comes to customer service, the roles of AI are vast and promising. Here are a few of the potential ways AI can revolutionize customer service in any industry, offering improved experiences and enhanced efficiency:
Chatbots and virtual assistants have emerged as increasingly vital customer service components. These innovative tools offer automated and instant responses to customer queries, greatly enhancing the overall experience. Powered by advanced AI technology, these smart assistants are designed to simulate human-like interactions, enabling more seamless and interactive communication. Not only can chatbots and virtual assistants answer frequently asked questions and guide website navigation, but they can also assist in purchasing decisions and even help schedule appointments. Their versatility allows them to handle various tasks, making them valuable business assets.
For example, if you are running an e-commerce store, leveraging AI-powered chatbots can provide round-the-clock customer support, significantly improving response times and reducing the need for human agents. Additionally, these intelligent assistants excel at delivering personalized and efficient assistance. They can analyze customer data and preferences to provide tailored recommendations and suggestions. This level of customization enhances the customer experience and fosters loyalty. By leveraging chatbots and virtual assistants, businesses can revolutionize how they engage with their customers, creating meaningful connections and building long-term relationships. With their ability to understand natural language, learn from interactions, and adapt to customer needs, chatbots, and virtual assistants are at the forefront of customer service innovation.
Sentiment Analysis, also known as opinion mining, harnesses the power of AI to analyze and interpret the emotional tone behind words. This innovative technology allows businesses to monitor the sentiments of their customers, understand their feelings and attitudes towards their products, services, or brands, and make proactive changes. Sentiment Analysis sifts through various unstructured data sources, such as social media posts, online reviews, customer surveys, and forum threads, identifying positive, negative, and neutral sentiments. It applies natural language processing, data analysis, and computational customer requests to extract and understand subjective information.
The resultant insights enable businesses to keep a pulse on customer satisfaction, resolve issues effectively, and tailor their offerings to meet customer expectations better. For example, if you run a hotel, you can leverage sentiment analysis to monitor guest reviews and feedback on social media platforms. Based on the sentiments expressed, you can identify areas of improvement and take corrective measures promptly. With AI-powered sentiment analysis, businesses can stay ahead of any negative publicity or customer dissatisfaction before it escalates into serious issues. This allows them to maintain a brand reputation and deliver exceptional customer service.
These predictive capabilities can be harnessed to provide proactive and personalized customer service, offering a competitive edge. By analyzing vast amounts of data, AI algorithms can predict customer behavior and identify potential issues before they occur. This enables businesses to address concerns proactively, prevent churn, and foster loyalty.
For example, if you run a subscription-based service, AI can analyze customer usage patterns and predict when they will likely cancel their subscription. Armed with this knowledge, you can reach out to them with targeted offers or personalized recommendations, increasing the chances of retaining them. AI’s predictive capabilities also extend to forecasting future trends and identifying customer needs and preferences. With this information, businesses can tailor their offerings and marketing strategies to meet customer demands better.
AI-powered systems have revolutionized the efficiency of routing customer inquiries. By leveraging advanced algorithms and machine learning, these systems can understand the nature of each query and analyze the expertise of customer service agents. This enables AI to seamlessly match customers with the most competent person to handle their specific concerns, ensuring a personalized and effective customer experience. For companies with large customer service departments, manually directing calls can be a time-consuming and error-prone process.
However, AI eliminates these challenges by automating the routing process. By minimizing misdirection, AI reduces customer frustration and allows quicker resolution of issues, leading to higher customer satisfaction. For example, if you run a large call center. AI can analyze customer inquiries, considering factors such as the query’s complexity and the available agents’ skills. This intelligent analysis enables AI to efficiently direct each customer to the agent with the most relevant expertise, thereby reducing wait times and enhancing satisfaction. With AI-powered routing systems, companies can optimize their customer service operations, providing a seamless experience for customers while improving the overall efficiency of their support teams.

These trends highlight how AI reshapes industries, revolutionizes decision-making processes, and transforms businesses in an increasingly data-driven world. From predictive data analytics to personalized customer experiences. Here are some emerging trends that vividly illustrate the immense potential impact of Artificial Intelligence (AI) on market forecasts:
AI is transforming the business landscape in remarkable ways. It is not just driving innovation but also creating new growth opportunities that were previously unimaginable. The impact of AI is evident across various aspects of business operations. AI has become an indispensable tool for market forecasting, from automating processes and predicting customer behavior to enhancing customer service experiences and improving decision-making. As technology advances at an unprecedented pace, businesses must adapt to these changes to stay competitive.
It is clear that AI will play a critical role in shaping the future of industries and revolutionizing how companies interact with their customers. By embracing AI, businesses can not only stay ahead of the competition but also deliver exceptional products and services that cater to their customer’s evolving needs and expectations. Investing in AI technology and leveraging its capabilities has become crucial for businesses to thrive in today’s fast-paced digital landscape. The future is here, and with AI, the possibilities are truly endless. It is an exciting time to be part of this transformative era, where AI paves the way for unprecedented growth, innovation, and success.
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning have become buzzwords in today’s tech-savvy world. However, there is often confusion and interchangeability in their use, leading to a lack of clarity about what each term truly represents. Artificial Intelligence (AI), the broader concept, refers to machines or computers performing tasks normally requiring human intelligence, such as understanding natural language, recognizing patterns, problem-solving, and decision-making.
Machine Learning (ML), on the other hand, is a subset of AI that focuses on the idea that machines can learn and adapt through experience. It centers on developing algorithms that allow computers to learn from and make decisions or predictions based on data. But how do these two concepts differ? And why is it crucial to distinguish between them in advanced computing and data analysis? This article will delve into the nuances of AI and machine learning, highlighting their differences, applications, and potential impact on our society.

Artificial Intelligence (AI) is the field of computer science that focuses on creating intelligent machines and systems that can think and act like humans. It involves developing algorithms, or rules, that enable computers to perform tasks that typically require human intelligence. These tasks can range from recognizing speech and images to making decisions and solving complex problems.
For example, AI is used in self-driving cars to recognize and interpret traffic signals, road signs, and other vehicles on the road. It uses complex algorithms and data analysis to decide when to accelerate, brake, or change lanes, all without human input. This application of AI not only improves efficiency but also has the potential to reduce accidents caused by human error.
Machine Learning model (ML) is a subset of AI that focuses on the idea that machines can learn and improve from experience without explicit programming. It involves developing algorithms that enable computers to learn from data, identify patterns, and mimic human intelligence or predictions based on this data.
For example, in the healthcare industry, ML analyzes massive amounts of medical data, including patient histories, test results, and symptoms, to help doctors diagnose diseases and recommend treatments. This application of ML not only helps healthcare professionals make accurate and timely diagnoses but also improves patient outcomes by reducing the likelihood of misdiagnoses.
While AI and ML are related concepts, significant differences must be understood. Some of the key differences between AI and ML are:
The scope of Artificial Intelligence (AI) is vast and constantly expanding. It aims to create intelligent machines and systems that mimic human thinking and decision-making processes. This includes natural language processing, computer vision, speech recognition, and problem-solving. AI has been applied in various industries, from healthcare to finance, to improve efficiency and automate complex processes. For example, in the financial sector, AI analyzes complex data and predicts stock market trends, helping investors make informed decisions.
On the other hand, Machine Learning (ML) has a narrower scope, focusing on enabling machines to learn from data without explicit programming. It involves developing algorithms to identify patterns and make decisions or predictions based on this data. This narrow scope makes ML more suitable for specific tasks such as image or speech recognition, fraud detection, and personalized recommendations. For example, popular streaming platforms like Netflix use ML algorithms to analyze user data and make personalized movie or TV show recommendations based on their viewing history and preferences.
The capacity for learning and adaptation differentiates AI and ML significantly. AI encompasses a broad spectrum, including systems that are taught or programmed with specific responses to all possible inputs. However, these systems cannot learn and adapt beyond their programming, making them less flexible in dynamic environments. Machine Learning takes this further as a subset of AI by incorporating the ability to learn from data and improve over time.
This learning occurs as the ML algorithms analyze vast datasets, identify patterns, and adjust their behavior or responses based on them, thereby learning from the data. An everyday example of this learning capability is found in email spam filters. These ML-powered filters learn from users’ actions of marking certain emails as ‘spam.’ Over time, the algorithm becomes increasingly accurate in detecting and filtering out unwanted emails, showcasing the power of machine learning’s adaptive learning ability.
Another significant difference between AI and ML lies in their data requirements. Artificial Intelligence systems typically require massive amounts of labeled data to function correctly and perform tasks effectively. Human experts often curate these datasets, making them expensive and time-consuming.
Machine Learning algorithms also require large datasets but do not necessarily need labeled data. Instead, ML algorithms can learn from unlabeled data by identifying patterns and making decisions or predictions based on this data. This ability makes ML more efficient, cost-effective, and adaptable than AI systems. For example, in fraud detection, ML algorithms analyze a large amount of financial transaction data to identify fraudulent patterns and flag suspicious transactions for further investigation.
AI and ML have diverse application areas, aligning with their unique capabilities. AI’s extensive scope enables it to create intelligent systems that mimic human behavior and abilities. As such, AI finds applications in areas like autonomous vehicles, where it’s used to interpret traffic data and make accurate navigational decisions. AI is also widely used in customer service, where chatbots can simulate human interaction, answering queries and providing information.
On the other hand, ML, with its ability to learn and improve, finds applications in industries where prediction and pattern recognition are crucial. For example, ML is used extensively in the financial market for predictive analysis, helping investors make informed decisions. It’s also commonly used in the healthcare industry for predictive diagnostics, helping physicians detect diseases in the early stages. Furthermore, ML powers recommendation systems on entertainment platforms like Netflix and Spotify, suggesting movies or songs based on user preferences and past behavior.
The human intervention also distinguishes AI and ML in their operation and functionality. In AI systems, human intervention is necessary at the initial stage for programming and setting rules. Once this is done, AI systems can operate independently, carrying out tasks and making decisions based on the provided rule set. However, they cannot go beyond their programmed instructions, and any adaptations or modifications require explicit human intervention.
For instance, a chess-playing AI is programmed with all possible moves and strategies, and it can independently play a game without further human input. Conversely, ML algorithms are designed to learn and adapt from data, reducing the need for constant human intervention. Instead of being explicitly programmed to perform a task, ML algorithms develop the ability by learning from data. However, they need human intervention for selecting features, choosing the right learning algorithm, or tuning parameters.
The complexity in design and the processing power needed differs between Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning. AI systems are generally more complex due to their broader scope and the need to simulate human decision-making processes. They demand higher processing power as they are required to handle diverse inputs and make complex decisions, just like a human brain would do. For instance, an autonomous vehicle that uses AI technology requires significant processing power to make real-time decisions based on various inputs from various sensors.
On the other hand, machine learning systems are designed with a narrower focus and are typically less complex. They are designed to identify patterns in large datasets and make predictions or decisions based on them. As such, the processing power required for ML systems often depends on the dataset size they need to analyze. In most cases, the processing power required for ML algorithms is significantly lower than AI systems, making them more efficient and cost-effective.

Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning are crucial in advancing technology, powering many innovative applications. Here are some ways AI and ML are transforming various industries and improving our daily lives:
Healthcare is undergoing a transformative revolution, with AI and ML driving this change. These advanced technologies are being deployed to improve patient outcomes, enhance operational efficiency, and usher in a new era of personalized medicine. AI is used to develop intelligent systems that expedite diagnosis and improve treatment plans. For instance, AI-driven image analysis tools are helping radiologists identify subtle patterns in medical images that the human eye might miss, thereby enabling early detection of diseases such as cancer.
Similarly, machine learning’s prowess in pattern recognition and predictive analytics allows it to analyze vast amounts of health data, deriving insights that help predict disease risk, understand disease progression, and personalize treatment strategies. A notable example is Google’s DeepMind Health project, which uses ML algorithms to predict kidney disease by analyzing patient data. Consequently, the advent of AI and ML in healthcare enhances patient care and pushes the boundaries of medical research and innovation.
Education is another sector that has seen significant advancements in integrating AI and ML technologies. These advanced technologies are revolutionizing traditional teaching methods, improving student engagement, and personalizing learning experiences. AI-powered chatbots are used to answer students’ queries in real time, providing immediate feedback and enhancing their understanding of difficult concepts.
Additionally, personalized learning algorithms use ML techniques to adapt to students’ individual learning styles, creating a customized curriculum that caters to their needs. A prime example of AI and ML in education is the online learning platform Coursera, which uses these technologies to deliver personalized courses and assessments to millions of learners worldwide. As a result, AI and ML are transforming the education sector by making it more accessible, engaging, and effective.
The financial sector is being redefined through Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning, revolutionizing traditional banking systems and introducing a new level of efficiency and security. AI and ML contribute significantly to fraud detection and prevention, employing complex algorithms that recognize suspicious patterns and activities that would be almost impossible for humans to identify. They also enable a hyper-personalized customer experience, with learning models analyzing past transactions and behaviors to anticipate users’ needs and offer targeted financial products or advice.
A notable example of this is the use of robo-advisors in wealth management. These AI-driven platforms use ML algorithms to manage a client’s investment portfolio intelligently, tailoring investment strategies according to changes in financial goals and market conditions. They offer a cost-effective alternative to traditional financial advisors and eliminate human bias, fostering a more transparent and efficient investment process. Consequently, integrating AI and ML technologies drives a significant shift in the finance sector, promoting innovation, enhancing customer service, and creating a more resilient and secure financial ecosystem.
The transportation sector is experiencing a major transformation by integrating AI and ML technologies. The advent of self-driving cars, powered by AI algorithms, is revolutionizing how we commute, improving road safety and efficiency. These advanced vehicles use sensors to gather real-time data about their surroundings and employ machine-learning techniques to make decisions in real-time, ensuring a smooth and safe ride. They also leverage predictive analytics to anticipate traffic conditions, optimize routes, and reduce travel time.
Additionally, AI-driven transportation systems enhance the logistics industry by streamlining supply chain processes, improving delivery times, and reducing costs. DHL’s smart logistics initiative is a prime example, using AI algorithms to optimize route planning and reduce carbon emissions in their delivery operations.
The retail sector is transforming remarkably by integrating Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning technologies. From predicting customer buying behavior to managing inventory and personalizing the shopping experience, AI and ML are reshaping the retail landscape. Advanced algorithms analyze customer data, helping retailers understand customers’ preferences and buying patterns. This information, in turn, enables retailers to offer personalized recommendations, enhancing customer engagement and driving sales.
Additionally, AI and ML are pivotal in inventory management, forecasting demand accurately, and preventing overstocking or understocking situations. The Amazon Go stores are an example of AI and ML revolutionizing the retail industry. These cashier-less stores leverage AI and ML for Just Walk Out Technology, where computer vision, sensor fusion, and deep learning algorithms automatically detect when products are taken from or returned to the shelves and keep track of them in a virtual cart. Upon exiting the store, customers are automatically charged for their purchases, offering an entirely new, seamless shopping experience.
Despite the remarkable benefits of AI and ML technologies, some challenges still need to be addressed. Some of the major challenges include:
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning are transformative forces reshaping various sectors of our society–from education and finance through transportation to retail. Their potential to automate, optimize, and innovate is undeniable. However, as these technologies evolve, addressing their challenges, such as data quality and bias, lack of transparency, ethical issues, and human oversight, is imperative.
While the path forward is complex, AI and ML’s benefits are too significant to ignore. Their integration into everyday life represents an opportunity to create more efficient, personalized, and inclusive systems, enhancing our quality of life and driving economic growth. Increasing trust in these technologies, ensuring their ethical use, and fostering responsible development will be vital in unlocking their full potential and steering our society toward a more innovative and equitable future.
In today’s ever-evolving workspace, remote working has become a game-changer. It’s redefining how we operate and collaborate, shaking up the traditional norms. Managing your team’s potential and ensuring their well-being and productivity is a whole new ball game. There’s no one-size-fits-all approach when it comes to remote teams. The key is understanding the unique nuances and intricacies of this way of working.
By implementing best practices and fostering trust, flexibility, and mutual respect, you can unlock previously untapped potential, boosting individual and collective performance. Navigating this new terrain may seem daunting, but this comprehensive guide will provide the tools and insights you need to lead your team in this digital age successfully. So, are you ready to transform your remote team into a powerhouse of productivity? Read on to unveil the secrets.

As businesses increasingly adopt a remote working model, it becomes paramount to understand the importance of managing remote teams effectively. Some key reasons include:
Boosted productivity remains one of the most compelling advantages of managing remote employees effectively. Employees working from their chosen environment can often focus better and produce higher quality work. They are free from the usual office distractions and can structure their day in a way that suits their personal working style.
For instance, a software developer might find they do their best coding during late-night hours, something that a traditional office setting wouldn’t accommodate. Giving them the freedom to work when they are most productive increases their output and improves their work quality. This is only possible when established best practices for remote work respect individual styles while ensuring overall team cohesion and goal alignment.
Enhancing work-life balance is another compelling reason to invest in best practices for remote teams. A well-balanced work-life scenario can significantly reduce stress and prevent burnout, often the pitfalls of the traditional 9-5 office setup. Remote work allows employees to create a schedule around their lives rather than trying to fit life around work. This flexibility means employees can attend to personal matters, such as picking their kids up from school or attending a mid-day yoga class, without impacting their work.
Take, for example, a graphic designer who thrives on creativity. By allowing them the freedom to take a mid-afternoon break to visit an art gallery for inspiration, they can return to their work refreshed and invigorated. This flexibility to harmonize personal interests and professional commitments can lead to enhanced job satisfaction, increased loyalty, and elevated performance levels, creating a win-win situation for both the employer and the employee.
Embracing the remote working model opens the door to a diverse, global talent pool, significantly broadening your team’s skills, experiences, and perspectives. This approach breaks down geographical boundaries that might otherwise limit your hiring options, giving you access to the best talent worldwide. For instance, a tech startup based in San Francisco could harness the expertise of a world-class cybersecurity specialist in Estonia, a seasoned AI engineer in India, or a leading UX designer in Denmark.
This wealth of global talent adds immense value to your team, fostering innovation, enhancing problem-solving capabilities, and paving the way for unique solutions that a homogeneous team might not conceive. The broader the spectrum of your team’s experiences and backgrounds, the greater your capacity to understand and cater to a diverse customer base and navigate the complexities of the global marketplace. Thus, effective remote team management promotes inclusivity and drives business growth and competitive advantage in today’s interconnected world.
Besides boosting productivity, enhancing work-life balance, and providing access to a diverse talent pool, effective remote team management can also reduce business overhead costs. Companies can save significant money by eliminating the need for physical office space and all its associated expenses, such as rent, utilities, maintenance, etc. This is particularly advantageous for startups and small businesses looking to minimize overhead costs and maximize profits.
For example, a digital marketing agency can operate with a fully remote team, eliminating the need for office space entirely. This reduces costs and allows companies to allocate more resources toward employee training, development, and well-being initiatives that ultimately benefit the team’s performance. Additionally, reduced overhead costs can lower client prices, making the business more competitive and attractive to potential customers.
Maintaining high employee retention rates is a strategic advantage that stems from effective remote team management. When employees are afforded the flexibility and autonomy inherent in working remotely, they often exhibit higher job satisfaction levels, leading to increased loyalty and lower turnover rates. This is particularly important in industries where the competition for top talent is fierce and the cost of hiring and training new employees is significant. For example, a remote employee working in the competitive tech industry.
They may have opportunities to switch to different companies, but the ability to work from home, avoid a stressful commute, and have a flexible schedule might be substantial factors that encourage them to stay with their current company. They can spend more time with their family, pursue hobbies, or further their education. This satisfaction with their work arrangement can make them less likely to seek opportunities elsewhere, leading to improved retention rates. Not only does this save the company resources regarding recruitment and training, but it also ensures the preservation of institutional knowledge and promotes a stable, experienced workforce.
Embracing remote work significantly enhances a business’s ability to weather unforeseen circumstances and maintain continuity in the face of disasters. Businesses with traditional office setups can face significant disruptions in scenarios such as a global pandemic or a natural disaster. However, companies implementing effective remote work practices can continue operations seamlessly, ensuring that productivity remains unhampered. For instance, during the COVID-19 pandemic, businesses with remote teams could adjust quickly and efficiently to the new work environment.
Additionally, remote working models mitigate risks associated with extreme weather conditions or other emergencies that may prevent employees from physically entering the office. This level of preparedness can give companies a competitive edge in the face of unpredictable events and ensure business continuity even in challenging times.

Managing a remote team successfully requires careful planning, effective communication, and the implementation of best practices. Below are key techniques to help you get the most out of your virtual team:
Establishing clear guidelines and expectations is important in managing a remote team effectively. These provide a framework to ensure all team members understand their responsibilities, deadlines, and expected work quality, promoting accountability and fostering a culture of trust and transparency. Guidelines should cover work hours, availability, communication protocols, productivity expectations, and tools to be used.
For instance, team members could be expected to respond to emails within a specified timeframe, or there could be designated hours for collaboration and meetings to accommodate different time zones. Expectations on project deadlines, quality of work, and regular update schedules should be unequivocally communicated.
Leveraging technology and tools is paramount for successful remote team management. In today’s digital age, a wealth of software and platforms is designed to facilitate collaboration, communication, project management, and productivity in a virtual work environment. Using these tools can help replicate the benefits of physical office space, maintaining team cohesion and ensuring projects stay on track.
For instance, project management tools like Trello or Asana allow teams to track progress, assign tasks, and manage deadlines effectively. Communication tools such as Slack or Microsoft Teams provide channels for real-time conversation, file sharing, and even video conferencing, keeping the lines of communication open and clear. Time tracking tools like Harvest or Toggl can help manage workloads and ensure fair distribution of tasks. It’s also important to utilize tools for secure data sharing, like Google Drive or Dropbox.
Fostering a positive team culture is of paramount importance for the success of a remote team. Establishing a palpable and cohesive culture within a remote workforce can be challenging, but it is an achievable objective with deliberate and strategic efforts. The key lies in creating a sense of belonging and connectivity among team members, which can be accomplished through regular communication, team-building activities, and recognizing and celebrating accomplishments.
For instance, virtual learning resources or happy hours can help maintain casual, non-work-related communication and create bonds similar to those in conventional office environments. Recognition of individual and team achievements, whether a shout-out in a team meeting or a public acknowledgment in a company newsletter, is crucial in fostering motivation and a cohesive team spirit. Furthermore, managers should strive to create an inclusive environment where every team member feels valued and heard and is encouraged to share personal life ideas and give feedback.
Effective communication is vital in managing a remote team, as it ensures that everyone is on the same page and allows for efficient collaboration. Effective communication becomes even more critical in virtual teams where non-verbal cues are absent. Managers should establish clear communication channels and ensure timely responses to inquiries to avoid delays or confusion. Additionally, it’s essential to use various communication methods and adapt to individual preferences.
For instance, some team members may prefer email for detailed updates, while others prefer quick chat messages or video calls. Additionally, managers should communicate regularly and proactively check in with team members to maintain a sense of connection and improve mental health.
Setting clear goals and tracking progress is essential to managing a remote team effectively. Establishing measurable and achievable objectives provides a roadmap for the team, outlining the tasks that need to be completed and the outcomes that are expected. Not only does this provide clarity and focus, but it also gives remote team members a sense of purpose, thereby boosting motivation and productivity. Furthermore, tracking progress allows managers to identify issues or bottlenecks early, ensuring that projects stay on track and deadlines are met.
This can be accomplished through regular check-ins, status reports, or project management tools visually representing progress. For instance, a team could use a tool like Jira, which allows for the creation of ‘Epics’ and ‘Stories,’ breaking down complex projects into manageable tasks. Team collaboration can then log their progress against these tasks, clearly showing how much work has been completed and what still needs to be done. This enables the team to stay aligned, fosters a sense of accomplishment as tasks are completed, and allows managers to provide timely support or resources where needed.
Promoting autonomy and trust is a vital aspect of managing remote teams effectively. When team members feel trusted and are given the autonomy to complete their tasks in ways that work best for them, they will likely be more engaged, productive, and satisfied. This can be achieved by setting clear expectations, providing the necessary resources, and allowing team members to complete their tasks without micromanagement.
Managers should also express confidence in their team’s abilities and recognize their efforts, which can foster a sense of trust and respect. For instance, regular check-ins could be transformed into opportunities for guidance and support rather than strict oversight. This approach bolsters self-confidence and motivation among team members and cultivates a sense of mutual trust and respect.
Properly onboarding and training new team members is a crucial aspect of remote team management. The onboarding process should be thorough, engaging, and designed to acquaint new hires with the company culture, mission, work processes, and tools. Providing adequate training to equip them with the knowledge and skills they need to perform their tasks effectively is also essential.
The key is to balance providing enough information to set them up for success without overwhelming them with too much data all at once. For instance, an effective onboarding process could involve a welcome session, an introduction to team members, walkthroughs of the most commonly used tools, and an overview of the company’s policies and procedures. Training sessions can also be conducted periodically as new tools are introduced or when the work process changes significantly.

While there are many remote work best practices, there are also some common pitfalls to avoid. These include:
Managing a remote team can present unique challenges, but the right approach and tools can increase productivity, satisfaction, and growth. The key lies in forming clear communication channels, setting achievable goals, promoting autonomy, and properly onboarding team members. It’s also crucial to avoid pitfalls like lack of communication, micromanaging, inadequate technology, and neglecting team dynamics.
By fostering a culture of trust, respect, and inclusivity and leveraging technology to bridge distances, managers can overcome the challenges of remote work and harness its potential benefits. As we navigate the evolving work landscape, these best practices will serve as the blueprint for teams to work remotely.
Every day, new cyber threats and attacks emerge, putting individuals and organizations at risk of losing valuable data and sensitive information. In today’s digital age, cybersecurity has become more critical. With rapidly advancing technology, cybercriminals have found new ways to exploit vulnerabilities in computer systems and networks. One such method that has gained traction in recent years is spooling. If you’re wondering what spooling is and how it impacts cybersecurity, keep reading to learn more.
A spooling attack is a type of security exploit where a malicious program or process imitates a legitimate one using its spool or buffer. In computing, spooling is a process where data is temporarily held to be used and executed by a device, program, or system. In a spooling attack, the attacker manipulates the spooling process to gain unauthorized access to a system, often to execute tasks without detection by masquerading as a legitimate operation.
These simultaneous peripheral operations can significantly threaten computer and network security. For example, a spooling attack can access a printer’s buffer and insert malicious code that can compromise the entire network. The attacker could also use spooling to redirect print jobs to a different location, potentially exposing sensitive information or disrupting business operations.
While print spooling is the most common form, other types are equally important in cybersecurity. Here are the most common types of spooling available:
Disk spooling attacks are cyber attacks that target the temporary storage space, or spool, on a computer’s hard drive. This type of attack can occur when an adversary gains access to the print spooler service on a computer and manipulates it to store malicious code or data in the spool file. This can then be used to compromise the system or steal sensitive information.
For example, a disk spooling attack could implant malware into a print job, which would then be executed when the document is printed and the spool file is accessed. This attack can be difficult to detect and prevent, making it a popular choice for cybercriminals seeking access to systems or data. To protect against disk spooling attacks, it is important to regularly update and secure the print spooler service on your computer and use strong security measures such as firewalls and antivirus software.
Network spooling attacks occur when an attacker gains access to a network’s print spooler service and manipulates it to redirect print jobs to their own malicious server. This allows the attacker to intercept sensitive information such as usernames, passwords, or confidential documents printed on the network. For example, an employee may unknowingly send a print job containing sensitive company information to the network printer, which is then redirected to the attacker’s server and stolen.
To prevent network spooling attacks, securing the print spooler service on all devices connected to the network and regularly monitoring for any unusual activity or unauthorized access attempts is important. Strong encryption methods can also protect against the interception of sensitive print jobs. In addition, it is crucial to educate employees about the risks of network spooling attacks and how to identify and report any suspicious activity. Secure printing methods, such as requiring user authentication before releasing a print job, can also help prevent these attacks.
Memory spooling attacks are similar to disk spooling attacks, but instead of targeting the hard drive’s temporary storage space, they target a computer’s memory. This attack can occur when an adversary gains access to the print spooler service and manipulates it to store malicious code or data in the computer’s memory. This can then be used to compromise the system or steal information.
To protect against memory spooling attacks, it is important to regularly update and secure the print spooler service on your computer and use strong security measures such as firewalls and antivirus software. Additionally, limiting access to the print spooler service and implementing strict user authentication measures can help prevent unauthorized access and manipulation of the system’s memory.
Web spooling attacks occur when an attacker gains access to a web server’s print spooler service and manipulates it to store malicious code or data in the temporary storage space on the server. This can then be used to compromise the server or steal sensitive information from users accessing the website. These attacks are particularly dangerous as they can target many users at once.
Regular updates and security measures for the print spooler service on web servers are crucial to prevent web spooling attacks. Secure coding practices and HTTPS encryption can also help protect against these attacks. Educating website users about the risks of web spooling attacks and how to identify and report suspicious activity is also important.
Buffer overrun attacks target a computer’s memory by overflowing a buffer, a temporary storage area used to access data. This attack can occur when an attacker gains access to the print spooler service and manipulates it to save data temporarily than the buffer can handle, causing it to overflow and potentially allowing the attacker to execute malicious code. To protect against buffer overrun attacks, regularly updating and securing the print spooler service and implementing strict user authentication measures can help prevent unauthorized access.
Denial of Service (DoS) attacks target a computer or network by flooding it with too many requests, overwhelming the system, and causing it to crash or become unavailable. This attack can occur when an attacker gains access to the print spooler service and manipulates it to send simultaneous peripheral operation print requests, thereby overloading the system. To protect against DoS attacks, regularly monitoring for any unusual activity on the print spooler service and implementing network security measures such as firewalls and intrusion detection systems is important.
Man-in-the-middle (MitM) attacks occur when an attacker intercepts communication between two parties, gaining access to sensitive information such as malicious printer driver login credentials or financial data. This attack can occur when an adversary gains access to the print spooler service and manipulates it to intercept print jobs containing sensitive information. To protect against MitM attacks, regularly updating and securing the print spooler service and strong encryption methods can help prevent attackers from intercepting sensitive data. It is also important to educate users about MitM attacks’ risks and how to communicate sensitive information securely.

While spooling attacks are a significant threat to computer systems, there are various factors that should be considered when dealing with them. These factors include ten of the following:
Spooling attacks can be categorized into two main types: print spooler and job spooler attacks. Print spooler attacks occur when an attacker gains unauthorized access to the print queue of a computer system, allowing them to intercept sensitive documents or inject malicious code into the printing process. On the other hand, job spooler attacks involve manipulating or deleting scheduled jobs in a system’s job queue.
This attack can lead to losing important data or disrupt critical processes. For example, an attacker could manipulate a scheduled backup job in a company’s server, resulting in the loss of important files and potentially crippling the entire network.
Ensuring a robust system configuration is paramount to preventing spooling attacks. This involves setting up stringent user access controls to limit unauthorized individuals from accessing critical queues like print and job queues. It’s also crucial to keep all software and hardware updated with the latest security patches, as outdated versions can offer a potential entry point for attackers.
For instance, the infamous Stuxnet worm was able to cause havoc in Iran’s nuclear program through a print spooler vulnerability in their Windows operating systems, which allowed the worm to spread and eventually cause physical damage to the centrifuges. Similarly, systems administrators should regularly review and clean job queues to prevent unauthorized or suspicious tasks from running. Periodically checking the integrity of system files and databases can also help detect any potential spooling attacks early. Hence, awareness, regular updates, and proactive monitoring are key in securing systems against spooling attacks.
Constant vigilance and regular updating of software and firmware are crucial in mitigating the threat of spooling attacks. Many of these attacks exploit vulnerabilities in out-of-date operating systems, server software, or application software, making systems with lapsed updates an attractive target for cybercriminals. For instance, an older version of a printer’s firmware may not have safeguards against unauthorized access to the print queue, making it susceptible to print spooler attacks.
An attacker could intercept sensitive documents, alter them, or even inject malicious code into the printing process. Similarly, outdated job scheduling software could be vulnerable to job spooler attacks. In these attacks, the perpetrator might manipulate or delete scheduled tasks, causing significant disruption to crucial operations.
Educating employees on the potential risks and tactics used in spooling attacks can reduce the likelihood of such attacks being successful. Many spooling attacks rely on social engineering techniques, where an attacker tricks an unsuspecting employee into divulging sensitive information or granting access to critical systems.
For example, a hacker may pose as an IT technician and ask an employee to provide their login credentials or run a fake software update that installs malware onto the system. Organizations can greatly reduce the risk of falling victim to spooling attacks by training employees to recognize these tactics. Employees should also be aware of the importance of regularly updating their passwords and not sharing them with anyone, as compromised login credentials are often used in spooling attacks.

Despite these considerations, spooling offers numerous benefits that make it a valuable tool in cyber security. Some of its key benefits include:
Spooling can greatly enhance system performance by optimizing data transfer and reducing bottlenecks. For example, print spooling allows multiple users to send print jobs simultaneously without waiting for each other’s documents to finish printing. This results in more efficient use of resources and faster document processing, improving overall productivity.
Similarly, disk spooling reduces the strain on the server by storing spooled data on external drives, freeing up system resources for other tasks. This can greatly improve the speed and performance of the system, especially in high-demand environments. Overall, spooling helps to streamline data transfer and reduce delays, resulting in increased system performance.
Spooling not only enhances security but also improves data management by centralizing it. Print spooling stores all print jobs in a centralized queue, reducing the risk of unauthorized access to confidential documents. Users can only gain access to their files through proper authentication, ensuring the protection of sensitive information.
Moreover, disk spooling facilitates easy encryption of data stored on external drives, adding an extra layer of security to the system. This feature helps prevent security breaches from unnecessary servers and safeguards sensitive data from unauthorized access.
Spooling offers enhanced flexibility in data transfer and storage. With print spoolers, users can conveniently queue their print jobs and access them from any network-connected printer. This is particularly beneficial in large organizations with multiple printers, allowing for greater convenience and flexibility in the printing process.
Disk spooling also simplifies data transfer between different systems or devices. For instance, if a user needs to retrieve a large file from a colleague’s computer, they can effortlessly spool it onto an external drive instead of waiting for the entire file to be transferred.
Resources are often limited in any organization, making it crucial to optimize their usage. Spooling helps with this by effectively managing system resources and reducing wastage. Windows print spooler can hold documents in the queue until the printer is available, preventing paper and ink waste from abandoned print jobs.
Disk spooling also allows for better management of storage space by optimizing the use of external drives. This can greatly reduce the need for additional storage devices, saving costs and resources.

While spooling offers numerous benefits, there are some pitfalls to avoid when implementing it in an organization. These include the following:
One of the key ways to avoid spooling attacks is by implementing strong access controls. This means limiting the number of users accessing sensitive data. By doing so, organizations can ensure that all non-administrative users are able to manipulate and interact with spooled information, reducing the risk of a security breach.
For example, a company may limit access to its payroll system, which utilizes spooling to print out employee paychecks. Only allowing authorized HR personnel access to this information greatly reduces the risk of a malicious insider gaining unauthorized access, which helps prevent spooling attacks.
It’s crucial for organizations to regularly monitor and audit their system logs to identify any potential spooling attacks. By closely monitoring system logs, unusual activity can be quickly identified and addressed before it leads to a larger security breach.
For instance, if an attacker gains access to the spooler in order to intercept sensitive documents, this activity would likely be recorded in the system log. Through regular monitoring and auditing, organizations can quickly catch and mitigate such attacks before they cause serious harm.
User-generated scripts can often be a source of vulnerability in spooling systems. This is because these scripts may contain malicious code that can exploit vulnerabilities in the spooler software. To avoid this, organizations should limit the use of user-generated scripts and instead rely on trusted, vetted scripts or applications for spooling tasks.
In addition, any user-generated scripts should be carefully reviewed and tested before being implemented in a production environment. This can help identify and eliminate potential security risks before attackers can exploit them.
Like with any software, it’s crucial to regularly update the spooler software to ensure that known vulnerabilities are patched, and new security features are implemented. Organizations should regularly review vendor releases and apply updates in a timely manner to keep their systems secure.
In addition, organizations should also monitor for any potential zero-day vulnerabilities or exploits that may target the spooler software. This can help mitigate any risks before attackers exploit them.
For those in the cyber security field, spooling is a valuable tool that offers numerous benefits. It can enhance system performance, improve security, offer flexibility, and better resource management. However, it is crucial to consider potential pitfalls and ensure proper implementation for maximum effectiveness.
Spooling can be a highly effective way of transferring data temporarily between computers. With the proper support and maintenance, it can be a reliable and secure system for organizations. By adhering to the best practices outlined in this article, businesses can ensure that their spooler systems are running smoothly and securely.
Businesses today face numerous threats to their IT systems, from natural disasters to human error and cyber-attacks. Organizations need a solid disaster recovery plan to mitigate the risk of these events disrupting business operations. However, having a plan is not enough. It is crucial for businesses to regularly test and update their disaster recovery strategies to ensure they are effective in times of crisis.
This article will look closely at disaster recovery testing and how it works. We will also discuss the importance of testing and provide tips for conducting successful disaster recovery tests.
Disaster recovery testing is a process of evaluating the effectiveness of a company’s disaster recovery plan. It involves simulating potential disasters or disruptions and analyzing how well the plan holds up in these scenarios. This can include scenarios such as power outages, cyber-attacks, equipment failures, and natural disasters.
For example, an organization may simulate a ransomware attack on their systems to see how well their data backup and recovery processes work. IT disaster recovery testing aims to identify any weaknesses in the plan and make necessary improvements before a real disaster strikes.

There are various types of disaster recovery testing, each with its objectives and methods. The most common types include the following:
Tabletop testing, also referred to as a structured walk-through, is a popular form of disaster recovery testing resembling a fun board game night. However, you’re preparing for potential IT catastrophes instead of battling imaginary dragons or constructing digital empires. During this test, key team members assemble physically or virtually and navigate through a specific disaster scenario. The primary objective is to ensure the effectiveness of the recovery plan steps while identifying any gaps or inconsistencies that may exist.
Importantly, this type of testing doesn’t involve actual systems or disruptions. Consider it a secure and consequence-free environment where you can explore various disaster scenarios. For example, you can simulate a scenario where a persistent ransomware attack has compromised your company’s data. As the story unfolds, your team will discuss each action step, assess its potential effectiveness, and adjust the strategy if necessary. The beauty of tabletop testing lies in its simplicity and flexibility, enabling frequent and comprehensive evaluation of your disaster recovery plan.
Simulation testing, also known as simulation exercises, involves a more comprehensive and detailed approach than tabletop testing. It aims to simulate realistic disaster scenarios involving actual systems and applications. The primary objective is to assess how well the company’s IT infrastructure can withstand the simulated disaster without significant disruptions to business operations.
During this disaster recovery test, the team may use specialized software or virtual machines to create a disaster scenario. For example, they can simulate a server crash or network outage and observe how the recovery plan performs in bringing systems back online. This type of testing provides a more accurate representation of how your disaster recovery plan will work in real-life situations.
Checklist testing, also known as readiness testing, is less of a dramatic production and more of a meticulous, methodical review of your disaster recovery plan. This type of testing involves going through the plan meticulously, item by item, to ensure that every aspect is ready to be deployed when disaster strikes. Think of it as a meticulous pre-flight examination by pilots, checking all the systems and instruments before takeoff.
It’s less about simulating a crisis and more about ensuring that your recovery plan is as ready as a well-packed parachute when that crisis comes. For instance, a company might use a checklist to verify that all necessary backups are regularly performed and stored off-site, all emergency contact information is up-to-date, and clear instructions for employees on what to do when disaster strikes. Although seemingly simple, checklist testing ensures no stone is left unturned in disaster recovery preparations.
Parallel testing involves running the primary and backup systems simultaneously and comparing their outputs to determine consistency. This type of DR testing is especially useful for complex IT environments where multiple interconnected systems need to work together seamlessly.
For example, a company might run its production and backup systems simultaneously and compare critical metrics like data accuracy and response times. If the results match, the backup system works correctly and can be relied upon in a disaster.

Effective disaster recovery testing is critical for businesses in today’s fast-paced, technology-driven world. It ensures that companies can continue their operations and serve customers even in times of crisis. There are several benefits to regularly testing your disaster recovery plan, such as:
Regular disaster recovery testing is essential for identifying any weaknesses in your plan. It allows you to proactively address potential issues and improve the effectiveness of your plan before a real disaster strikes. For example, during a simulation exercise, an organization may realize that their backup systems are not as robust as they thought, leading them to upgrade their hardware and software.
Additionally, testing can highlight any gaps in communication or unclear roles and responsibilities during a crisis. This allows organizations to make necessary adjustments and ensure that everyone knows their role and what is expected of them. By identifying weaknesses through testing, companies can strengthen their disaster recovery plan and increase their chances of successfully recovering from a disaster.
Regular disaster recovery testing is not only crucial for identifying weaknesses, but it also helps build confidence in the plan itself. By regularly testing and seeing positive results, organizations can gain trust in their disaster recovery strategies and feel more prepared to handle potential crises. This confidence extends beyond the IT department and can positively impact the entire company.
For example, if you are an e-commerce business, conducting regular disaster recovery testing can assure you that your website will remain functional and secure during a cyberattack or server failure. This confidence is valuable for your customers and employees, as they know that you have a reliable plan to keep the business running smoothly even in times of crisis.
Many industries, such as healthcare and finance, have strict regulatory requirements for disaster recovery planning. Regular disaster recovery testing is necessary to ensure companies comply with these regulations. It also provides evidence that they are taking the necessary steps to protect sensitive data and maintain business continuity.
By regularly testing their disaster recovery plan, organizations can avoid hefty fines and legal repercussions while ensuring the safety and security of their data. It also helps build trust with customers and stakeholders, who want to know that their information is safe in the hands of a responsible and compliant company.
Disaster recovery testing not only tests the technical aspects of a plan but also allows organizations to train employees on their roles and responsibilities during a crisis. Employees can become more familiar with the plan and their specific tasks by involving all relevant departments in testing. This preparation is crucial during an actual disaster when time is of the essence, and everyone needs to know what to do.
For example, if a company’s IT department undergoes regular disaster recovery testing, it can train other departments on accessing essential systems or data in an emergency. This cross-departmental training ensures the entire organization is prepared to handle a disaster.
Technology is constantly evolving, and so are potential threats to business operations. Regular IT disaster recovery testing ensures that all backup systems and procedures are up-to-date with the latest developments in technology and security. It helps companies identify outdated systems or applications that may cause delays or failures during a crisis. By regularly testing their disaster recovery plan, organizations can avoid potential problems and ensure their systems are always ready to face any disaster.
Service level agreements (SLAs) are contracts between a company and its service providers, and they outline the services provided, response times, and consequences for not meeting agreed-upon terms. Regular disaster recovery testing allows organizations to evaluate their SLAs with service providers and ensure they meet their obligations.
If a disaster strikes, companies must know that their service providers will respond promptly and effectively. By regularly testing these agreements, organizations can identify gaps or areas for improvement in their SLAs and address them before a disaster occurs.
Communication is key during a crisis, and disaster recovery testing allows organizations to test their communication channels and processes. It ensures that all departments, employees, and stakeholders receive timely updates and instructions during a disaster.
For example, testing communication channels may involve sending mock alerts or conducting a conference call to simulate a crisis. By regularly testing these channels, companies can identify issues with their communication systems and make necessary improvements. This ensures everyone stays informed and can take appropriate action during a real disaster.
Disaster recovery testing is not a one-time task; it should be an ongoing process that encourages continuous improvement. Regular testing allows organizations to collect data and feedback from each simulation, identify areas for improvement, and make necessary adjustments. This ensures the disaster recovery plan stays relevant and effective in the face of new risks and challenges.
Companies must regularly review and improve their disaster recovery plans as technology and potential threats evolve. By doing so, they can stay ahead of potential disasters and confidently navigate any crisis that may come their way. So, don’t wait for a disaster to strike; start testing your plan to ensure your business’s survival and success. As the saying goes, “An ounce of prevention is worth a pound of cure.” So, be proactive and regularly test your disaster recovery plan to avoid potential disasters and keep your business running smoothly in times of crisis. After all, it’s better to be safe than sorry!
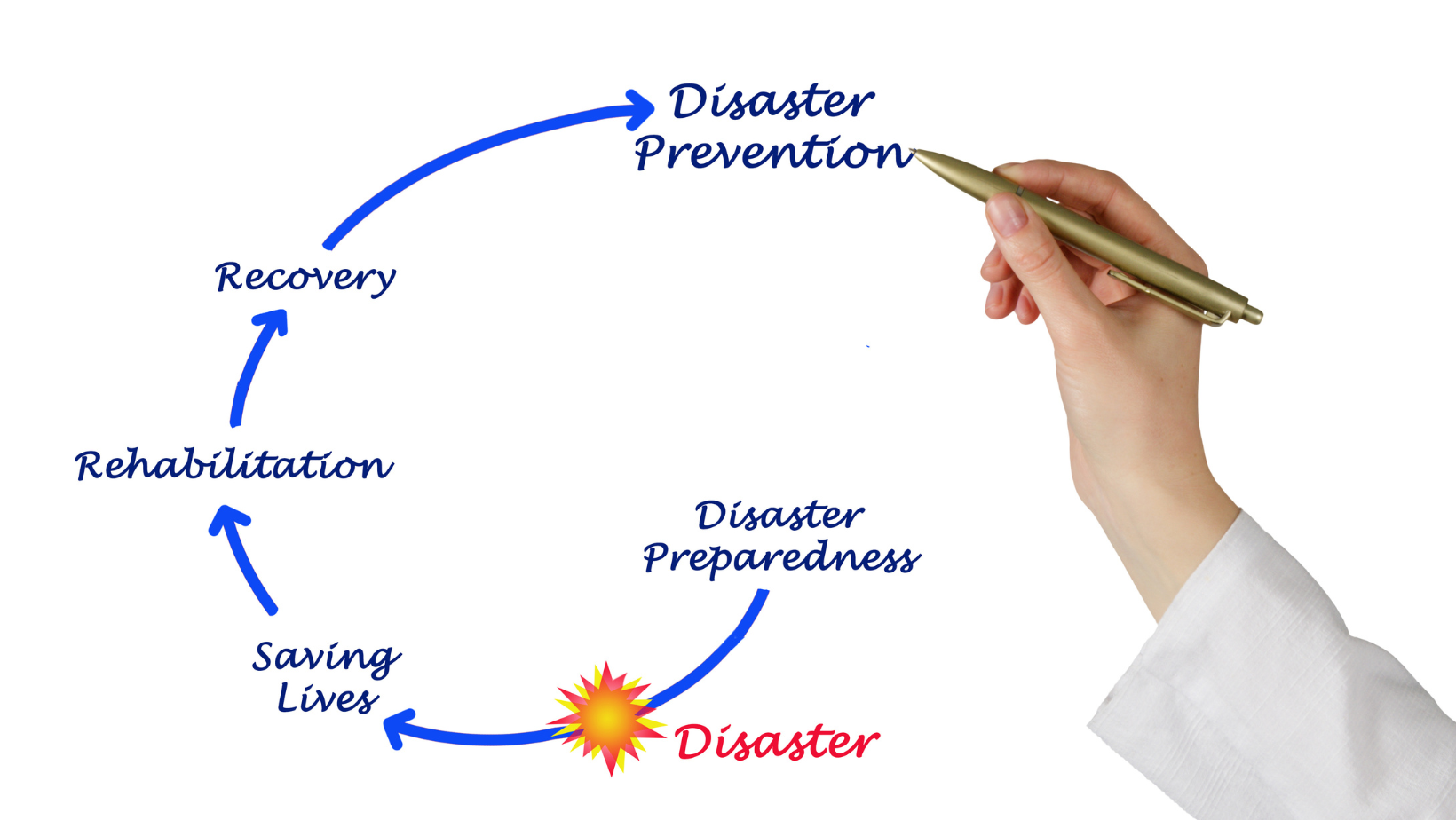
Businesses can follow these steps to conduct IT disaster recovery testing effectively:
Before conducting IT disaster recovery testing, it is crucial to identify the key components of your organization’s infrastructure and operations. These may include servers, databases, applications, networks, and critical business processes. By understanding these components’ dependencies and relationships, you can prioritize which aspects must be tested first.
For example, if a company relies heavily on online transactions for revenue generation, its e-commerce recovery sites and payment gateway should be top priorities for testing. This ensures that these critical components can be recovered quickly and effectively to minimize the impact on business operations during a disaster. Identifying key components also helps organizations understand potential points of failure and proactively address them before they become a bigger issue during a real disaster.
Next, organizations must define their objectives for disaster recovery testing. This may include minimizing downtime, maintaining data integrity, or ensuring minimal impact on customers and stakeholders. Once the recovery objectives are clear, companies can create various disaster recovery scenarios to test the effectiveness of their disaster recovery plan in different situations.
For example, a scenario could involve a natural disaster that causes a power outage and impacts the organization’s ability to access critical data and systems. This allows organizations to simulate real-world situations and analyze the effectiveness of their plan in addressing different types of disasters.
Disaster recovery testing involves multiple departments and individuals, each with specific roles and responsibilities during a crisis. It is essential to clearly define these roles and assign them to designated disaster recovery team members during the testing process. This ensures a coordinated effort and effective communication during a disaster.
For instance, one person may be responsible for initiating the disaster recovery plan, another for data backup and restoration, and another for communicating with stakeholders. Clearly defining these roles helps organizations identify gaps or overlaps in responsibilities and address them before a crisis occurs.
After conducting the disaster recovery process, organizations must document the results and make necessary improvements to their plan. It is essential to record any issues or challenges encountered during the simulation and determine how to address them in future tests.
Documenting results also allows companies to track their progress and see how their disaster recovery plan has evolved. This information can be useful in identifying patterns and trends, making informed decisions, and continuously improving the plan to ensure maximum effectiveness.

As with any process, there are common mistakes that organizations should avoid when preparing a disaster recovery testing checklist:
Many businesses make the mistake of only testing their disaster recovery plan once a year or less frequently. This can be detrimental as it does not account for technological changes and potential vulnerabilities that may arise throughout the year. Regular testing allows companies to improve their plans and address new threats or risks continuously.
Disaster recovery testing is not just an IT department’s responsibility; it involves multiple departments that play a crucial role in an organization’s operations. It is important to involve representatives from these departments in the testing process to ensure all aspects of the business are accounted for and properly integrated into the disaster recovery testing scripts.
While having a recovery time objective plan in place is essential, it is equally important to have a backup plan for unexpected situations. For example, what if the designated team member responsible for initiating the disaster recovery plan is unavailable during a crisis? Companies must have backup plans to ensure they can still effectively manage and recover from a disaster.
As mentioned earlier, technology and potential threats are constantly evolving. Therefore, it is crucial to regularly update the disaster recovery test plan to account for these changes. Failing to do so may result in an outdated plan that is not effective during a real disaster.
IT disaster recovery testing is critical for businesses to ensure they can effectively and efficiently recover from potential disasters. By following the steps outlined above and avoiding common mistakes, organizations can proactively prepare for crises and minimize their impact on operations. Remember, it is always better to be safe than sorry when it comes to disaster recovery planning.
So, make sure to regularly test your plan and continuously improve it to stay ahead of any potential disasters. Don’t wait until it’s too late; start planning and testing your disaster recovery plan today!
As technology continues to advance rapidly, the world is becoming increasingly interconnected. With this interconnectivity comes advancements in communication and unprecedented access to information. However, with these benefits come numerous risks, particularly in cyber security. As we rely more and more on technology for all aspects of our lives, from personal communication to financial transactions, it has become imperative that we understand and address the potential threats posed by cyber-attacks.
In this article, we will explore the future of cyber security and how it is evolving to meet the ever-changing landscape of technology. We will delve into some of the major developments in this field, as well as potential challenges and solutions. Keep reading to learn more!
In the past decade, cyber security has become a critical topic in both the public and private sectors. With sensitive data breaches and cyber-attacks on major corporations, governments, and individuals becoming more prevalent, it is clear that no one is immune to these threats. In fact, according to a report by Cybersecurity Ventures, global cybercrime damages are expected to reach $6 trillion annually by 2021. Here are current trends and challenges in the field of cyber security:

Ransomware attacks have emerged as one of the gravest threats in the realm of cyber security. This malicious tactic involves hackers infiltrating systems and encrypting critical data, effectively holding it hostage until a ransom is paid. The frequency and severity of these attacks have seen an alarming increase in recent years. A prominent example is the WannaCry ransomware, which infected over 300,000 computers in more than 150 countries, incurring damages worth millions of dollars. The impact of these attacks transcends financial burdens, as they compromise sensitive information and erode trust in technology and digital systems.
What makes ransomware attacks even more treacherous is their constant evolution. Hackers persistently seek new ways to circumvent security measures, rendering organizations vulnerable in their attempts to protect themselves. As technology continues to advance, it is expected that ransomware attacks will correspondingly grow more sophisticated and widespread in the future.
Another major concern for cyber security experts is the growing number of Internet of Things (IoT) devices used in homes and businesses. These devices, such as smart home systems, connected appliances, and wearable technology, are vulnerable to cyber-attacks if not properly secured. A study by HP found that 70% of IoT devices were vulnerable to attack.
This poses significant cybersecurity threats as more and more devices become connected through the internet, creating a larger attack surface for hackers to exploit. With the increasing use of IoT devices in critical infrastructure, such as healthcare and transportation, the consequences of a successful attack could be catastrophic. As the number of these devices continues to grow, their security must be prioritized to mitigate potential risks.
Gone are the days when cyber-attacks were solely carried out by individual hackers looking for notoriety or financial gain. Today, state-sponsored attacks have become a significant concern in cyber security. Governments orchestrate these attacks with malicious intent towards other countries or organizations.
Such attacks can cause widespread damage and disruption on a large scale, as seen in the 2017 NotPetya attack, which targeted Ukraine’s energy sector but ended up affecting companies worldwide, causing billions of dollars in damages. With the advancement of technology and the increasing use of cyber warfare tactics, it is expected that state-sponsored cyber attacks will continue to be a major threat in the future.
The shortage of skilled professionals in the field of cyber security is a crucial challenge that needs to be addressed in order to ensure a safer digital world. With the rapid growth of the global cybersecurity workforce, there is an ever-increasing demand for skilled professionals to protect against cyber threats and attacks. However, according to a report by Cybersecurity Ventures, there will be 3.5 million unfilled cybersecurity jobs globally by 2021.
This lack of skilled cybersecurity professionals leaves organizations vulnerable as they struggle to find qualified individuals to manage their intrusion detection systems. It also means that those working in the industry are often overwhelmed with responsibilities, increasing the risk of human error. Addressing this issue will require a collaborative effort from governments, organizations, and educational institutions to train and attract more individuals into the field.
The cybercrime economy is a rapidly growing problem that poses a significant threat to the future of cyber security. Hackers and cybercriminals are becoming more organized, sophisticated, and profitable in their attacks, creating a booming underground market for stolen data and information. For example, in 2019, hackers stole over 5 million credit card records from US-based companies and sold them on the dark web for approximately $40 each.
This shows the lucrative nature of cyber risks and the need for increased preventive measures to protect against these criminal activities. As technology continues to advance, we can expect this trend to continue, making it crucial for organizations to invest in robust security measures and stay updated on the latest threats to prevent becoming victims of this growing economy.
As more organizations move their data and operations to the cloud, security risks also increase. The shared nature of the cloud means that a single vulnerability can affect multiple clients, making it an attractive target for cybercriminals. Additionally, inadequate security measures from cloud service providers can leave organizations exposed to attacks.
To mitigate these risks, businesses must carefully choose their cloud service providers and ensure they have proper cybersecurity strategies. They must also regularly assess and update their security measures to protect against threats.
While external cyber attacks often receive more attention, insider threats are just as dangerous and challenging to detect. These individuals have authorized access to an organization’s systems or information but use that access maliciously for personal gain or revenge.
Insider threats can cause significant damage, both financially and in terms of reputation. To combat this issue, organizations must have strict access controls and continuously monitor their systems for suspicious activities.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) has become a buzzword in the technology world, with its ability to automate processes and improve efficiency. However, as AI continues to evolve and expand its capabilities, it also presents significant challenges for cyber security. One of the main concerns is that hackers can use AI technology to launch more sophisticated attacks that are harder to detect and prevent.
AI-powered phishing attacks can gather personal information from social media platforms and create highly personalized and convincing emails, making it easier for individuals to fall victim. To counter this threat, organizations must invest in advanced AI-based security measures to keep up with potential attackers. This includes using machine learning algorithms to analyze patterns of behavior on their networks and proactively identify any suspicious activities before they turn into full-blown attacks. The future of cyber security heavily relies on our ability to use AI technology to improve our defense mechanisms and stay ahead of malicious actors.

Given these current trends and challenges, the future of the cybersecurity industry may seem daunting. However, there are significant developments and advancements being made to address these issues and ensure a safer digital world for all. Here are some key trends that we can expect to see in the future:
As technology continues to advance, so do the methods employed by cyber attackers. Traditional security measures are inadequate in defending against these ever-changing threats. This is where artificial intelligence (AI) emerges as a potent tool in the realm of cyber security. By leveraging AI systems, vast amounts of data can be analyzed and elusive patterns can be identified, augmenting threat detection and prevention to new heights.
IBM’s Watson for Cyber Security serves as a prime example of such an AI system. Through the utilization of ingenious machine learning techniques, security data is comprehensively analyzed, enabling the identification of potential threats that frequently elude human analysts. With the rapid expansion of Internet of Things (IoT) devices and interconnected systems, AI assumes a pivotal role in safeguarding these vulnerable technologies.
With the rise of cyber-attacks, traditional passwords and authentication methods have proven inadequate in protecting sensitive information. Biometric technology, such as fingerprint scanning and facial recognition, is becoming increasingly popular in enhancing security measures. These biometric identifiers are unique to each individual and are much more difficult for hackers to replicate than a password.
Not only are they more secure, but biometrics also provide a more convenient user experience by eliminating the need for multiple passwords. In addition, advancements in AI have made it possible to use behavioral biometrics, which analyzes how a person interacts with their device and can detect unusual behavior that may indicate an attempted hack.
As encryption is crucial in keeping data safe from cybersecurity risks, cloud computing may be the future of secure communication. Unlike traditional computers that use binary bits (0s and 1s), quantum computers use qubits, which can exist as 0s and 1s simultaneously. This enables them to process data at an exponentially faster rate than classical computers.
With this speed, quantum computers can easily break existing encryption methods, making them a significant threat to cyber security. However, researchers are also exploring how quantum technology can create unbreakable encryption methods that will provide stronger protection against attacks.
Aside from technological developments, education and awareness are crucial in mitigating cyber security risks. Many data breaches occur due to human error, such as falling for phishing scams or using weak passwords. By educating individuals on how to recognize and prevent these attacks, the overall security of digital systems can be improved.
With the increasing number of cyber threats in today’s world, everyone needs to understand the importance of cyber security and take responsibility for their safety online. This includes organizations implementing proper training programs for their employees to ensure they have the knowledge and skills to protect sensitive information. Governments should also prioritize cyber security education in their policies to create a more secure digital environment for citizens.

As we continue to navigate the ever-changing landscape of technology and cyber threats, there are a few crucial factors to consider. These include ten of the following:
Collaboration between industries is an essential aspect of addressing the future of cyber security. With the increasing interconnectedness of our global economy, it has become crucial for different industries to work together to protect against cyber attacks. A prime example of successful collaboration is the financial sector’s partnership with law enforcement agencies to combat financial fraud and cybercrime.
In 2018, a group of banks and law enforcement agencies worked together to take down a notorious cybercriminal organization that had stolen over $100 million from banks worldwide. This collaboration allowed for the pooling of resources and information, leading to the arrest and prosecution of those responsible for the attacks.
Education and training are crucial factors in addressing the future of cyber security. With the ever-evolving landscape of technology, individuals and organizations need to stay updated on the latest threats and preventive measures. This requires continuous education and training programs that cover topics such as identifying social engineering tactics, implementing proper security protocols, and responding to cyber-attacks effectively.
One example is the Cybersecurity Talent Initiative launched by the US Government in 2019. This program offers student loan assistance to individuals pursuing cybersecurity careers in exchange for working in a federal agency for a minimum of two years. By investing in education and training, we can ensure a skilled workforce that can keep up with the constantly evolving cyber threat landscape. Additionally, educating individuals about basic cybersecurity practices can help prevent attacks, as employees are often the weakest link in an organization’s security.
Government involvement and regulation play a vital role in addressing the future of cyber security. Governments must work with industry leaders to establish regulations and policies that hold organizations accountable for their cybersecurity measures. This includes enacting laws that require companies to implement proper security protocols and regularly update them to protect against emerging threats.
An example of government involvement is the European Union’s General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), which sets strict guidelines for how companies handle personal data and imposes significant fines for non-compliance. Such regulations not only ensure better protection for individuals’ data but also encourage businesses to take cybersecurity seriously.
Technological advancements, both in terms of cyber defenses and threats, will continue to shape the future of cybersecurity. With emerging technologies such as AI, blockchain, and quantum computing, there is a constant race between defenders and attackers to stay ahead.
On the one hand, these technologies can provide more robust security measures through methods like behavioral biometrics and unbreakable encryption. On the other hand, they also pose new challenges as cybercriminals find ways to exploit them for their gain. Therefore, it is crucial to invest in research and development and stay updated on emerging technologies to ensure effective defense against evolving threats.
As technology continues to advance and cyber criminals become more sophisticated, cybersecurity remains a pressing concern for the future. To safeguard against potential attacks, organizations must proactively invest in advanced security measures, including AI-based technologies. Collaboration across industries, ongoing education and training, and government involvement all play vital roles in addressing the ever-evolving landscape of cybersecurity.
While we cannot predict the exact trajectory of cybersecurity, one thing is certain: it demands unwavering vigilance, adaptability, and collaboration to stay one step ahead of threats. Although the future may appear uncertain, implementing the right strategies ensures a safer digital world for everyone. As the adage goes, “An ounce of prevention is worth a pound of cure,” and this rings particularly true in the realm of cybersecurity. Let us join forces in constructing a secure future for all.
Cyber security is a hot topic in today’s digital age and for good reasons. With the ever-increasing number of cyber-attacks and data breaches, it has become crucial for businesses and organizations to protect their sensitive information from potential threats. One of the key steps in securing your digital assets is conducting a comprehensive cyber security risk assessment.
This process involves identifying potential risks and vulnerabilities in your systems, analyzing their potential impact, and implementing necessary measures to mitigate them. In this article, we will discuss the importance of conducting a cyber security risk assessment, as well as provide you with practical tips on how to conduct one effectively. Keep reading to learn how you can safeguard your business against cyber threats.
A cybersecurity risk assessment is a pivotal piece in the jigsaw puzzle of organizational security. It’s no less than a detailed, methodical evaluation of your system’s vulnerabilities, potential threats from mischievous hackers, and the disastrous consequences that might follow if these elements were to conspire against your cybersecurity defenses. Think of it as a routine medical check-up but for your digital health. Just as you’d want to identify any health risks before they manifest into more serious conditions, a risk assessment helps you to spot weak points in your cyber security architecture before they are exploited, leading to data breaches.
The process goes beyond a simple identification of risks. It is a comprehensive exercise that involves ranking these risks based on their likelihood and potential impact. It also entails strategically formulating a robust defense mechanism to mitigate them. By conducting a Cyber Security Risk Assessment, you are not just reacting to threats but proactively strategizing to ensure the protection of your organization’s valuable digital assets against the relentless onslaught of cyber-attacks. This approach keeps you one step ahead of troublemakers in the cyber world.

Conducting a Cyber Security Risk Assessment brings numerous benefits to your organization, both in the short and long term. From identifying potential threats to creating an action plan for mitigating them, here are some of the key roles and benefits you get when you perform a cybersecurity risk assessment:
One of the primary roles of conducting a Cyber Security Risk Assessment is to identify potential risks that can threaten your organization’s digital assets. This process goes beyond just identifying obvious vulnerabilities and takes a deep dive into all possible scenarios that could lead to a data breach. For example, imagine your company stores sensitive customer information such as credit card numbers and personal details on its servers.
A risk assessment would not only identify external threats like malware or hacking attempts but also internal risks such as employee negligence or unauthorized access by disgruntled employees. By thoroughly assessing and identifying these potential risks, you can take proactive steps to mitigate them before they become a cyber-attack. So, it’s essential to conduct regular risk assessments to stay one step ahead of cyber threats and safeguard your organization’s valuable data.
A Cyber Security Risk Assessment goes beyond identifying risks and their potential impact. It also helps you to develop a comprehensive defense strategy to mitigate these risks effectively. This can include implementing security measures like firewalls, encryption, and multi-factor authentication, as well as creating procedures for regular data backups and employee training on cyber security best practices.
If the risk assessment identifies weak passwords as a potential vulnerability in your organization’s systems, you can implement stronger password requirements and provide employees with training on how to create secure passwords. By taking proactive steps based on the results of the risk assessment, you can strengthen your overall defense against cyber threats.
Prioritizing risks is an essential aspect of conducting a Cyber Security Risk Assessment. Not all risks are created equal, and some may have a more significant impact on your organization’s digital assets than others. By ranking the identified risks based on their likelihood and potential impact, you can focus your resources and efforts on mitigating the most critical threats first.
If the cyber risk assessment reveals that a specific software vulnerability has a high likelihood of being exploited and can result in a significant data breach, you can prioritize fixing this vulnerability immediately rather than addressing lower-risk issues first. This targeted approach allows you to allocate your resources effectively and efficiently, ensuring maximum protection for your organization’s valuable data.
In today’s regulatory landscape, organizations are required to comply with various data protection laws and regulations, such as GDPR and HIPAA. Cybersecurity risk assessments can help your organization identify potential gaps in compliance and take corrective action before facing penalties and fines.
If your risk assessment reveals that your organization is not adequately protecting sensitive customer information, you can strengthen security measures and ensure compliance with data protection regulations. This not only protects your organization from legal consequences but also builds trust with customers who expect their data to be handled securely.
While conducting a risk assessment may require an initial investment of time and resources, it can save your organization from significant financial losses in the long run. By identifying and mitigating potential risks early on, you can avoid costly data breaches and associated expenses such as forensic investigations, legal fees, and damage control.
In addition, conducting a risk assessment can identify inefficient or redundant security measures that may be costing your organization money without providing adequate protection. By streamlining your defense strategy based on the results of the risk assessment, you can improve cost efficiency while maintaining robust security.
A Cyber Security Risk Assessment not only identifies potential risks to your organization’s digital assets but also helps to create an action plan for mitigating these risks effectively. This proactive approach ensures that in case of a cyber-attack or other disaster, your organization has a solid business continuity plan to minimize downtime and maintain operations.
If your risk assessment reveals that a ransomware attack could disrupt your organization’s operations and lead to significant financial losses, you can implement measures like regular data backups and disaster recovery strategies. This ensures your business can quickly recover and continue operating even after a cyber-attack or other disruptive event.
When you conduct cybersecurity risk assessments, you demonstrate to stakeholders that your organization takes data protection seriously. It shows you are proactive in identifying potential risks and taking steps to mitigate them effectively.
This can enhance stakeholder confidence in your organization’s ability to protect sensitive information, ultimately improving trust and reputation. In the long term, this can also lead to increased business opportunities and a competitive advantage in the market.

Now that you understand the importance of a Cyber Security Risk Assessment, here are some steps to help you conduct one effectively:
The first step in conducting cyber risks Assessment is identifying and prioritizing your organization’s digital assets. This can include sensitive data, systems, networks, and applications. By understanding the value and importance of each asset, you can better assess the potential impact of a cyber-attack and prioritize risks accordingly.
If your organization heavily relies on a specific software system for its operations, this may be considered a high-priority asset that requires extra protection against potential vulnerabilities.
Once you have identified and prioritized your assets, the next step is identifying potential threats that could compromise their security. This can include external threats such as hackers or internal threats such as employee negligence.
If your organization deals with sensitive customer data, potential threats could include a cyber-attack aimed at stealing this information or an employee mistakenly sharing confidential data.
After identifying potential threats, the next step is to assess any vulnerabilities within your organization’s systems and processes. Vulnerabilities can include outdated software, weak passwords, or lack of encryption. By conducting vulnerability assessments, you can identify weaknesses that potential threats could exploit.
If your organization uses an outdated operating system that is no longer supported with security updates, this presents a vulnerability that hackers could exploit. By addressing this vulnerability through patching or updating the system, you can mitigate the risk of a cyber-attack.
It’s important to conduct regular vulnerability assessments as new cybersecurity risks emerge and technology evolves. This allows you to stay ahead of potential risks and ensure your organization’s digital assets are adequately protected.
Once you have identified potential threats and vulnerabilities, it’s essential to rank the risks based on their likelihood of occurrence and potential impact. This allows you to prioritize which risks require immediate action.
For high-risk issues, develop mitigation strategies that address both short-term and long-term risk assessment reports. For example, if an outdated software system poses a high risk to your organization’s data security, a short-term goal may be to update or replace the system, while a long-term goal could be implementing regular software updates to prevent future vulnerabilities.
The final step in conducting a Cyber Security Risk Assessment is implementing your risk management plan. This involves putting into action the strategies developed in the previous step.
It’s important to regularly review and update your risk management strategy as new threats emerge and technology evolves. This ensures your organization is continuously improving its defense against potential risks.
It’s crucial to document the entire risk assessment process. This includes documenting each step taken, any risks identified and mitigated, and any changes made to your organization’s systems and processes.
Documentation not only helps track progress but also serves as a reference for future risk assessments. It allows you to see how your organization’s security has improved over time and identify areas that may require further attention.

Conducting a Cyber Security Risk Assessment is an ongoing process that requires dedication and continued effort. To ensure the effectiveness of your risk assessment report, here are some of the best practices to keep in mind:
Involving all stakeholders in the Cyber Security Risk Assessment process is crucial for its success. This includes not only IT professionals but also employees from other departments, such as finance, legal, and human resources. By involving a diverse group of stakeholders, you can gain different perspectives and expertise to identify potential risks and develop effective mitigation strategies.
For example, if your organization involves its marketing team in the risk analysis process, The marketing team may be able to identify potential cyber threats related to social media accounts used for promoting the company’s brand. They can then work with the IT department to put measures in place to prevent these threats from occurring. In this way, involving all stakeholders can help address blind spots that may have been overlooked otherwise.
A proactive approach is crucial when conducting a Cyber Security Risk Assessment. This means regularly reviewing and assessing potential risks rather than waiting for an actual cyber-attack to occur. By being proactive, you can identify security risks and address them before potential threats exploit them.
For example, instead of waiting for an employee to fall victim to a phishing scam, you can proactively conduct training sessions and implement security measures to prevent such attacks from occurring in the first place.
Cybersecurity is constantly evolving, with new threats emerging every day. It’s essential to stay informed about the latest trends and developments in the industry to ensure your risk assessment remains relevant and effective.
This includes staying up-to-date on new technologies, security measures, and best practices. Additionally, keeping track of current cyber-attacks and data breaches in your industry can help identify potential risks specific to your organization.
As mentioned earlier, ranking risks based on their likelihood of occurrence and potential impact is crucial in developing an effective risk management plan. It’s essential to prioritize high-risk threats that could have a severe impact on your organization’s operations or reputation.
If your organization deals with sensitive customer data, a potential data breach would be considered a high-risk threat that should be addressed immediately.
While no one wants to think about worst-case scenarios, it’s important to plan for them when conducting a Cyber Security Risk Assessment. This means considering potential catastrophic events that could severely impact your organization’s operations or lead to its downfall.
By planning for the worst-case scenario, you can develop strategies to prevent such events from occurring and create a contingency plan should they happen.
In addition to involving all stakeholders within your organization, it can also be beneficial to seek external expertise when conducting a Cyber Security Risk Assessment. This could include hiring consultants or working with cybersecurity firms specializing in risk assessment.
External experts can provide unbiased opinions and insights into potential risks that may have been overlooked internally. They can also offer recommendations and best practices based on their experience working with other organizations in similar industries.
Conducting a Cyber Security Risk Assessment is an essential step in ensuring the protection of your organization’s data and systems. It involves identifying potential risks, developing strategies to mitigate them, and continuously monitoring and updating your risk management plan.
By following best practices such as involving all stakeholders, being proactive, staying informed, prioritizing risks, planning for worst-case scenarios, and seeking external expertise, you can conduct a thorough and effective risk assessment that helps safeguard your organization against cyber threats. Remember to document the entire process to track progress and serve as a reference for future assessments. Stay vigilant and regularly review your risk management plan to ensure maximum protection against ever-evolving cyber threats. Happy assessing!
The responsibilities surrounding cloud disaster recovery solution are somewhat complicated since it doesn’t lie in the hands of the cloud service provider alone but also put some role in the hands of cloud vendors and the customers that hire the services of cloud vendors as a CSP for disaster recovery services.
It’s essential to learn everything that surrounds getting a cloud disaster recovery solution or service to help you get the most out of it for your business. We bring you this information in this article.
So let’s dive into the essentials that you should keep in mind when delving into the realm of cloud disaster recovery point objectives. It affects services and a cloud provider disaster recovery solution for your business.
Cloud disaster recovery to restore data disaster recovery involves the use of cloud systems and services to improve the data recovery of the IT infrastructure-affected data and systems in cases where a disaster occurs.
Cloud disaster recovery mostly utilizes cloud-based dr for steps like replicating data and IT systems that are essential for business functionality and can’t be replaced when an issue occurs, regardless of the disaster recovery plan or the recovery time objective.
The replications also cover the applications that the business uses to carry out normal operations and that are used to handle the data and critical systems required to restore the optimal functionality of businesses in the shortest timeframes creating a seamless workflow.
Making plans for the disaster recovery side of cloud-based systems that store backup data after a disaster strikes is essential when running a business, especially one that heavily relies on data to function properly and serve your target audience to the fullest.
Proper disaster recovery planning for cloud-based systems helps you reduce the downtimes and power outages that your operations will encounter when a disaster occurs. The resilience to resume normal operations against issues that lead to power outages and data loss is enhanced by a cloud disaster recovery plan.
Disaster recovery for cloud base systems doesn’t have its responsibilities lying on the various cloud computing providers, the various cloud-based cloud dr, and the cloud computing services alone but also on the customers who use it for their business as this creates the best results depending on the situation at hand.
They are responsible for the business impact analysis and analyzing the potential disasters the cloud-based system can experience. On the business impact analysis on the whole cloud disaster recovery point objective, customers are responsible for fine-tuning the virtual systems to match the requirements and goals they have set for the business to ensure it matches their initial plan to prevent miscommunication and misinterpretation.

It’s essential that both the CSPs and customers deeply understand the roles they play in resume operations and that of the other party, including the importance of these roles and how they affect the result obtained at the end of the whole cloud disaster recovery process.
It helps both parties understand who to hold responsible when there are issues with certain aspects of the cloud disaster recovery plan and operations, making each party stay accountable for their actions and spreading the responsibilities out.
It also creates room for both parties to make a cloud disaster recovery plan more efficiently since each person knows what to handle and the others can align their operations to the preceding operations creating a fast and coordinated workflow to ensure the cloud disaster recovery process is completed faster, more efficiently, and in the best way possible.
Cloud dr service providers have the responsibility of managing and protecting the data and other cloud dr storage-based systems that include virtual servers, virtual machines, the networking infrastructure, and data centers and perform maintenance for the server hardware and other necessary aspects.
They are tasked with ensuring that the various cloud storage-based systems, virtual machines, network infrastructure, and data centers are secured, protected from attacks and potential disasters, reliable, and can be depended on when they are needed the most without losing them to natural disasters.
CSPs work on optimizing the infrastructure of businesses, which includes the data centers and facilities that the business turns to store backup data for their operations. Data centers are essentials that provide support to cloud dr systems and operations which makes it important for them to be optimized and managed properly to ensure business continuity and prevent data loss.
The CSPs analyze these data centers and provide a rundown to resume business operations create improvements in the current makeup along with a strategy to properly manage them in the long term and use them for disaster recovery plans when the event of a disaster occurs.
They also are responsible for handling migration from physical backup data in centers to cloud-based storage systems, which is a channel to improve the ease of backup data and disaster recovery plans during natural disasters.
It falls among the responsibilities of CSPs to create a network infrastructure that is robust enough to handle the connectivity and demands of the cloud disaster recovery services, including the data centers and facilities for running a perfectly operational business in cloud environments.
This responsibility includes proper management of the equipment infrastructure that is required for optimum operations of cloud technologies like routers and network switches while deploying them at the physical location at the right time with the appropriate strategies implemented for the best results. They work to prevent network downtimes and to support the seamless operational functionality of cloud environments for the business.
Servers in the server capacity secondary data center system of a business serve as the backbone to store every piece of information that the business has and accesses regularly when serving its customers with deliverables.
The maintenance of the servers is also an important task that CSPs handle, which includes the updating of software that the server and the local secondary data center itself are based on, along with the firmware and security systems required to keep it protected at all times.
The health of the server and secondary site itself, its performance, and the utilization of resources it infrastructure are also among the responsibilities of CSPs in this category to ensure the server and secondary local data center itself’s health stays optimal at all times.
Reliability is also essential as the CSPs have to be accountable just as much as the customers, and them being the experts need to have a certain level of a disaster recovery plan and strategy as a service and agreement that shows their operations and covers other responsibilities that they perform as they handle your disaster recovery operations.
CSPs are responsible for providing these service level agreements, which should match the business and state the responsibilities of both parties as it is a defined contract required to put both parties on the same page before the disaster recovery workflow commences.
It’s also essential to help you as the customer know the operational patterns of their managed service providers and see how it helps your disaster recovery plan as a service, and your business improve to serve your customers and also meet your already set goals.
CSPs are also responsible for handling all situations with redundancy and providing fault tolerance mechanisms when the need arises in the business during disaster recovery for cloud-based systems. The responsibility to handle redundancy leads them to work with different levels like the redundancy on hardware to duplicate certain physical components like servers and specific network devices and then deploy them to secondary site to provide a substitute to use when the main component encounters an issue.
The others are redundancy on networks and server capacity, which involves using multiple internet service providers to create a backup for a potentially affected cloud-based cloud dr and a secondary data center with redundant network and server capacity, and lastly is data redundancy which involves replicating the data across multiple geographical locations, several platforms and multiple data centers, to serve as a backup during a disaster.
The CSPs cloud vendor that you hire also needs to have their very own cloud disaster recovery plan, strategies, and plans for their cloud infrastructure to ensure that they are set in stone and capable of handling the issues that you have with a cloud dr disaster affecting your business.
It is the responsibility of the CSPs to set this disaster recovery plan and strategies in place as it is essential in proving that their cloud infrastructure they can take your business infrastructural development without encountering any issues during the disaster recovery process.
They perform analysis to determine the potential impact of a disaster and how it affects businesses by tailoring it to what you offer, then create a disaster recovery strategy and plan to counter that impact by including data replication and backup along with your infrastructural redundancy and replication to keep your business data safe when the disaster finally hits your cloud-based systems.

The process of backing up data has some of its responsibilities laying in the hands of the cloud providers and customers since you, as a customer, will need to pick out the essential pieces of backup data or blocks of data that needs backing up to ensure business continuity and protection business-critical data.
Your selection will most likely be based on the recommendations provided by the CSPs for disaster recovery strategies but the final decision to choose which among the recommended disaster recovery strategies, dr tools or procedures you can go with according to your budget is left to you.
The responsibility for validating the archiving policies that should be attached to your data protection is also left in your hands since disaster recovery planning is a service. It is essential to note that for the proper working of the CSPs operations.
The configuration of the cloud environment and technologies for the system and applications are also the responsibilities of you as a customer since it is your business, and you know best what your goals are as a business continuity well as the operations you carry out to serve your customers.
Configuring the various cloud computing resources, IT infrastructure, and applications that you use for your business requires you to fill in business details that should likely not be made available to the cloud providers, vendors, or external parties and handle them yourself or by an in-house employee is the best since the accountability will not be held by the cloud provider or CSPs.
Security and remote access are also a responsibility that lies with cloud and traditional dr approaches and significant business costs you as a cloud dr provider and a traditional cloud dr customer as you need to keep remote access to the business data secured from third parties as intervention and breaches might occur especially when there are no specified compliance regulations and SLAs in place.
Creating an efficient channel of communication between you and your CSPs allows both parties to work better and deliver the best results during traditional disaster recovery and cloud disaster recovery effects since both parties will be on the same page and work seamlessly, which is the premise for good collaboration between traditional disaster recovery and cloud disaster recovery. It is essential first to create a proper and efficient channel of communication when working so as to keep the other party informed about the progression of the traditional disaster recovery time objective operation for your cloud-based systems in a timely manner in order to prevent any misunderstandings and misalignments when implementing specific techniques. Matching the roles and responsibilities of each party also works to coordinate the planning process when it comes to cloud disaster recovery and makes the testing process seamless, as each responsibility can be completed and accounted for with proper collaboration.
You need to keep your business protected from the law by prioritizing the regulations in the state and industry in that your business lies which makes it essential to consider the legal requirements and compliance instructions that the CSPs bring to your business operations when performing disaster recovery techniques for your cloud storage and cloud computing based systems. The CSPs must meet the standards of the data protection and privacy laws which span the general protection of data availability in the European Union and other essential regulations attached to the safeguarding of data on the various cloud computing and storage platforms.
Its also essential that the disaster recovery techniques and methods match with the laws in the jurisdiction where your business is located along with the regions that cloud computing and storage providers and their services span. There should also be agreements based on contracts that show the compliance statements of the business and should include clauses for vendors, monitoring auditing, and certain other important aspects for legal consideration.
You should ensure that the service level agreements that are provided to you are as detailed as possible to cover every aspect that is essential to the cloud platform based disaster recovery process. It should express clear expectations of what you should achieve and what the CSPs are willing to offer you in the agreement so you know what exactly your payment is for during the cloud platform disaster recovery process.
The agreement should also provide performance metrics that the CSPs will use to monitor and validate the effectiveness of the methods DR services that they plan to implement in your cloud cloud-based dr disaster recovery strategy for you to be aware of how effective it is and how far it will go in providing you with the best results that you can find google the cloud- traditional dr disaster recovery platform when disaster strikes itself.
It’s also essential that the SLAs include the availability of the CSPs. Hence, you know how much time they are giving to handle your issue, along with the timeframe that they have set aside to make their service available to you.
There are certain practices that help you enjoy the best cloud-based disaster recovery service from your CSPs, especially if you want to make the most of your investment. One of these best cloud dr practices that you should consider implementing is defining the objectives for the various of your cloud disaster recovery plan and traditional cloud disaster recovery, strategies, workflows, and of your data as it gives you a rundown of what you want to achieve when the traditional disaster recovery process is done. A clear goal to look forward to and plan your activities around regularly backing up your data should be listed among the objectives you have set out.
You should also try as much as possible to replicate the primary data center and applications that your business uses while utilizing redundant infrastructure to deploy your applications across several availability zones. It’s also great to do periodical testing of your cloud disaster recovery plan to validate it in case there are outdated, and this requires you to monitor the process while maintaining the optimal process for each recovery point objective and its successful completion.